1 of 9
Downloaded 131 times








Recommended
ą¤čĆąŠą│čĆą░ą╝ą╝čŗ ą┐ąĄčĆąĄą┐ąŠą┤ą│ąŠč鹊ą▓ą║ąĖ ą▓ ą£ąōąŻ



ą¤čĆąŠą│čĆą░ą╝ą╝čŗ ą┐ąĄčĆąĄą┐ąŠą┤ą│ąŠč鹊ą▓ą║ąĖ ą▓ ą£ąōąŻAnna Proff
╠²
ą¤čĆąŠą│čĆą░ą╝ą╝čŗ ą┐ąĄčĆąĄą┐ąŠą┤ą│ąŠč鹊ą▓ą║ąĖ ą▓ ą”ąĄąĮčéčĆąĄ ąĖąĮč鹥čĆą░ą║čéąĖą▓ąĮčŗčģ č鹥čģąĮąŠą╗ąŠą│ąĖą╣ ążąśą»ąĀ ą£ąōąŻ ąĖą╝ąĄąĮąĖ ą£.ąÆ. ąøąŠą╝ąŠąĮąŠčüąŠą▓ą░. ąöąĖą┐ą╗ąŠą╝ ą£ąōąŻ. ą¤čĆąĖčüą▓ąŠąĄąĮąĖąĄ ąĮąŠą▓ąŠą╣ ą║ą▓ą░ą╗ąĖčäąĖą║ą░čåąĖąĖ ą¤ąĢąöąÉąōą×ąōąÉ. ąóąĄą╝ą░: ąśąÜąó ą▓ ą┐čĆąĄą┐ąŠą┤ą░ą▓ą░ąĮąĖąĖ ąĖąĮąŠčüčéčĆą░ąĮąĮčŗčģ čÅąĘčŗą║ąŠą▓. Teacher's competences



Teacher's competencesgueste538c3
╠²
The document discusses competencies needed for teachers and trainers. It identifies seven categories of competencies: special professional, general educational, didactic and psycho-didactic, diagnostic and interventional, social/psychosocial/communicative, managerial/normative, and professional/personality cultivating. It also discusses key elements of teacher training models, including responding to societal changes and learner needs. International collaboration is presented as important for teacher training, such as joint research, student/staff mobility, and double degree programs.Teacher's Competencies



Teacher's CompetenciesDr.Suresh Isave
╠²
the show describes the competencies expected in Indian teacher by NCTE. These competencies are one of the base of teacher education in India.TEACHER COMPETENCE AND PERFOMANCE



TEACHER COMPETENCE AND PERFOMANCEshaxee Mchilo
╠²
A DOCUMENT FOR THE SOME OF DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE NOTION OF TEACHER COMPETENCE AND TEACHER PERFORMANCE.Competency Based Teacher Education and METHODS Assessing Teacher Competence.



Competency Based Teacher Education and METHODS Assessing Teacher Competence.Priyanka Nain
╠²
This document discusses competency-based teacher education. It defines teaching competency as an overall assessment of a teacher's classroom performance based on their subject matter knowledge, teaching methods, questioning skills, use of aids, student participation, personality, classroom management, and objective clarity. Competent teachers are pupil-oriented and able to develop instructional materials, use varied teaching methods, and evaluate student progress. Teaching competencies improve education quality, help students and teachers achieve objectives, improve teacher status, and aid personal and professional development. Competencies are categorized as cognitive, performance, consequence, and affective-based. Methods for assessing teacher competence include telling, lecture, discussion, demonstration, and problem-solving approaches.Competency Based Teacher Education



Competency Based Teacher Educationredekera
╠²
The document discusses competency-based teacher education (CBTE) as a framework for music teacher education. It describes the CBTE program evolving at the University of North Florida, which is individualized, field-based, and focuses on measurable competencies and teaching modules. An informal evaluation of the UNF program concluded that implementing a CBTE approach for music teacher education is worthwhile despite the effort involved.TeachersŌĆÖ Competences to Meet Teaching Learning Quality 



TeachersŌĆÖ Competences to Meet Teaching Learning Quality Mas Noer
╠²
This presentation talks about what teachers should have to achieve quality teaching and learning process. Standards for teacher competence in educational assessment of student



Standards for teacher competence in educational assessment of studentMichael Recolito
╠²
This document outlines standards for teacher competence in student assessment developed by three educational organizations. It defines standards as principles accepted by relevant professional groups. The standards state that teachers should be skilled in choosing, developing, administering, scoring, and interpreting various assessment methods, using results to inform instructional decisions and grading. Teachers should also be able to communicate results and recognize inappropriate assessment practices. Teaching and Learning of 21st-century Competencies in Schools 



Teaching and Learning of 21st-century Competencies in Schools Benedict Chua
╠²
The document discusses the teaching and learning of 21st century competencies in Singaporean schools. It outlines a framework for 21st century competencies and how they can be taught through the total curriculum, including co-curricular activities and the Programme for Active Learning. It also discusses building teacher capacity to teach these competencies and ensuring alignment between pre-service teacher training and in-service professional development. Moving forward, the focus will be on further equipping teachers to teach 21st century skills to students.Learning evolution



Learning evolutionLjudmilla Rozhdestvenskaja
╠²
ą¤ąŠą┐čŗčéą░ąĄą╝čüčÅ ąŠčüą╝čŗčüą╗ąĖčéčī, ą║ą░ą║ ąĖąĘą╝ąĄąĮąĖą╗ą░čüčī čłą║ąŠą╗čīąĮą░čÅ čāč湥ą▒ąĮą░čÅ čüčĆąĄą┤ą░ ąĘą░ č鹊čé ą┐ąĄčĆąĖąŠą┤, ą║ąŠč鹊čĆčŗą╣ ą╝ąĮąŠą│ąĖąĄ ąĖąĘ čāčćą░čüčéąĮąĖą║ąŠą▓ "ąŠčģą▓ą░čéčŗą▓ą░čÄčé" čüą▓ąŠąĖą╝ čüąŠą▒čüčéą▓ąĄąĮąĮčŗą╝ ąŠą┐čŗč鹊ą╝ - čāčćąĖč鹥ą╗čīčüą║ąĖą╝ ąĖą╗ąĖ čāč湥ąĮąĖč湥čüą║ąĖą╝. ą¤ąĄčĆąĄą┤ ą▓ą░ą╝ąĖ ą┐ąŠą┐čŗčéą║ą░ - čäąĖą║čüąĖčĆąŠą▓ą░čéčī ąĖ ąŠč鹊ą▒čĆą░ąĘąĖčéčī ą▓ čüčģąĄą╝ą░čģ ąĖ ą║ąŠčĆąŠčéą║ąĖčģ č鹥čüčéą░čģ ą▒čŗčüčéčĆąŠ ą╝ąĄąĮčÅčÄčēčāčÄčüčÅ "ą║ą░čĆčéąĖąĮčā čłą║ąŠą╗čīąĮąŠą│ąŠ ą╝ąĖčĆą░". ąĪ ą┐ąŠą╝ąŠčēčīčÄ ą┐čĆąĄąĘąĄąĮčéą░čåąĖąĖ ą┤ą▓ą░ čāčćąĖč鹥ą╗čÅ ą┐ąŠčüčéą░čĆą░ą╗ąĖčüčī ą┐čĆąĄą┤čüčéą░ą▓ąĖčéčī čüą▓ąŠąĄ ą▓ąĖą┤ąĄąĮąĖąĄ 菹▓ąŠą╗čÄčåąĖąĖ čāč湥ą▒ąĮąŠą╣ čüčĆąĄą┤čŗ ąĖ č鹥čģ ąĖąĘą╝ąĄąĮąĄąĮąĖą╣ ą▓ ą╝ąĄč鹊ą┤ąĖą║ą░čģ, ą┐ąŠą┤čģąŠą┤ą░čģ ą║ ąŠą▒čāč湥ąĮąĖčÄ, ąŠčéąĮąŠčłąĄąĮąĖčÅčģ ą▓ąĮčāčéčĆąĖ čāč湥ą▒ąĮąŠą│ąŠ ą┐čĆąŠčåąĄčüčüą░, ą║ąŠč鹊čĆčŗąĄ ą┐čĆąŠąĖčüčģąŠą┤ąĖą╗ąĖ ą▓ čĆą░čüčüą╝ą░čéčĆąĖą▓ą░ąĄą╝čŗą╣ ą┐čĆąŠą╝ąĄąČčāč鹊ą║ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĖ. ąÆąĄčüčī ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĮąŠą╣ ąŠčéčĆąĄąĘąŠą║ čĆą░ąĘą▒ąĖčé ąĮą░ 4 ą╝ąŠą┤ąĄą╗ąĖ-ą┐ąĄčĆąĖąŠą┤ą░, čĆą░ąĘčāą╝ąĄąĄčéčüčÅ, čŹč鹊 čĆą░ąĘą▒ąĖąĄąĮąĖąĄ - ą░ą▓č鹊čĆčüą║ąŠąĄ - ąŠąĮąŠ čāčüą╗ąŠą▓ąĮąŠ ąĖ čüčāą▒čŖąĄą║čéąĖą▓ąĮąŠ! ąÆą░ąČąĮąŠ, čćč鹊 ą▓čüąĄ čŹčéąĖ ą╝ąŠą┤ąĄą╗ąĖ čüąĄą│ąŠą┤ąĮčÅ "čüčāčēąĄčüčéą▓čāčÄčé" ą▓ čüąŠąĘąĮą░ąĮąĖąĖ čāčćąĖč鹥ą╗čÅ ąŠą┤ąĮąŠą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĮąŠ, ąĮą░ą║ą╗ą░ą┤čŗą▓ą░čÅčüčī ą┤čĆčāą│ ąĮą░ ą┤čĆčāą│ą░ ąĖ čćą░čüčéąĖčćąĮąŠ ą┐ąĄčĆąĄą║čĆčŗą▓ą░čÅčüčī, ąĖ čāčćąĖč鹥ą╗čÄ ąĮčāąČąĮąŠ ąĮą░ą╣čéąĖ čüą▓ąŠąĄ ą╝ąĄčüč鹊, čüą░ą╝ąŠąŠą┐čĆąĄą┤ąĄą╗ąĖčéčīčüčÅ, ą▓ ą║ą░ą║ąŠą╣ ą╝ąŠą┤ąĄą╗ąĖ ąŠąĮ čüąĄą▒čÅ ą▓ąĖą┤ąĖčé, ą║ ą║ą░ą║ąĖą╝ ąĖąĘą╝ąĄąĮąĄąĮąĖčÅą╝ ąŠąĮ ą│ąŠč鹊ą▓?
Models of teaching



Models of teachingAileen Asim
╠²
The document discusses various teaching models including information processing models, behavioural models, personal models, and social models.
It provides details on several information processing models such as Atkinson and Shiffrin's model of memory, Gagne's information processing model, and different types of inquiry teaching models. Behavioural models covered include direct instruction, mastery learning, and programmed instruction models. Personal models summarized are non-directive teaching, developing positive self-concepts, and the project model. Lastly, the social model discusses group teaching, cooperative learning, and simulation methods like sociodrama and role-play.
The document provides an overview of key teaching models with the goal of guiding teachers in planning and5th standard of teacher Assessment 



5th standard of teacher Assessment dayo barbie
╠²
This document discusses assessment for teachers. It defines assessment as measuring something numerically to make a judgment. There are different types of assessment including formative, formal, traditional, summative, and informal. The document outlines teacher knowledge around assessment, including using various assessment techniques to evaluate and improve teaching and learning. It provides examples of how to implement assessments using modern technologies and the significance of assessment for helping students improve their skills. Finally, it describes the qualities of a high quality teacher in relation to assessment, such as believing assessment can improve teaching, making lesson plans, assessing students accurately, and making evidence-based decisions.Speaking: Getting attention



Speaking: Getting attentionFerry Pus Pus
╠²
Getting attention perfectly requires respecting others, showing empathy, speaking audibly and clearly with humility. To gain attention, one must care about the message and prepare it well while also caring for those being addressed. Really wanting to communicate well requires being ready to take risks of being attacked, challenged, or ignored, but also risks of being congratulated, promoted or put in charge. The basics of communicating well involve understanding your audience and yourself, rehearsing your message, and knowing how to entrance and hold your audience's attention through your message and presence. Once attention is gained, it must be maintained through consistent expression of who you are in all communications.ąōąĖąĮ ąĪ.ąś. ą¤ąŠą┤ą│ąŠč鹊ą▓ą║ą░ ą╝ą╗ą░ą┤čłąĖčģ čłą║ąŠą╗čīąĮąĖą║ąŠą▓ ą║ ąĖąĮč鹥ą╗ą╗ąĄą║čéčāą░ą╗čīąĮčŗą╝ čüąŠčüčéčÅąĘą░ąĮąĖčÅą╝: ą┐čĆąŠą▒ą╗ąĄ...



ąōąĖąĮ ąĪ.ąś. ą¤ąŠą┤ą│ąŠč鹊ą▓ą║ą░ ą╝ą╗ą░ą┤čłąĖčģ čłą║ąŠą╗čīąĮąĖą║ąŠą▓ ą║ ąĖąĮč鹥ą╗ą╗ąĄą║čéčāą░ą╗čīąĮčŗą╝ čüąŠčüčéčÅąĘą░ąĮąĖčÅą╝: ą┐čĆąŠą▒ą╗ąĄ...ąĪą▓ąĄčéą╗ą░ąĮą░ ąźą░ąĮčīą║ąŠ
╠²
ą£ą░č鹥čĆąĖą░ą╗čŗ IVčĆąĄčüą┐čāą▒ą╗ąĖą║ą░ąĮčüą║ąŠą│ąŠ čĆąŠąČą┤ąĄčüčéą▓ąĄąĮčüą║ąŠą│ąŠ č乥čüčéąĖą▓ą░ą╗čÅ ą┐ąĄą┤ą░ą│ąŠą│ąĖč湥čüą║ąŠą│ąŠ ą╝ą░čüč鹥čĆčüčéą▓ą░ ą┤ą╗čÅ ąĮą░čćą░ą╗čīąĮąŠą╣ čłą║ąŠą╗čŗBridging the theory-practice gap in LIS education: a UCT experiment - Jaya Ra...



Bridging the theory-practice gap in LIS education: a UCT experiment - Jaya Ra...HELIGLIASA
╠²
This document discusses bridging the theory-practice gap in library and information studies (LIS) education through an experiment at the University of Cape Town (UCT). It provides context on the relationship between theory and practice in LIS education. At UCT, the LIS school is organizationally located within UCT Libraries in an effort to better integrate theory and practice. The document evaluates this model and lessons learned, focusing on how UCT Libraries and the LIS school have worked to address the theory-practice gap and prepare LIS graduates for the changing nature of academic libraries.UTPL-METHODOLOGY AND DIDACTIS I-I-BIMESTRE-(OCTUBRE 2011-FEBRERO 2012)



UTPL-METHODOLOGY AND DIDACTIS I-I-BIMESTRE-(OCTUBRE 2011-FEBRERO 2012)Videoconferencias UTPL
╠²
Universidad T├®cnica Particular de Loja
Carrera: Ingl├®s
Docente: Mgs. Orlando Vicente Lizaldez E.
Ciclo: S├®ptimo
Bimestre: Primero
čüąŠąĘą┤ą░ąĮąĖąĄ ą║ą░ą╗ąĄąĮą┤ą░čĆčÅ Google



čüąŠąĘą┤ą░ąĮąĖąĄ ą║ą░ą╗ąĄąĮą┤ą░čĆčÅ GoogleąÆą░ą╗ąĄąĮčéąĖąĮą░ ąĀąŠą╝ą░ąĮąŠą▓ą░
╠²
ąÆ ą┐čĆąĄąĘąĄąĮčéą░čåąĖąĖ ą┐čĆąĄą┤čüčéą░ą▓ą╗ąĄąĮ ą┐čĆąŠčåąĄčüčü čüąŠąĘą┤ą░ąĮąĖčÅ ą║ą░ą╗ąĄąĮą┤ą░čĆčÅ čü ą┐ąŠą╝ąŠčēčīčÄ čüąĄčĆą▓ąĖčüą░ Google CalendarRole of teacher in intellectual development ppt



Role of teacher in intellectual development pptFarooq Mustafa
╠²
This document discusses the role of teachers in intellectual development according to several theories. It covers Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development in children and how it can be applied in the classroom. Key concepts in Piaget's theory include scaffolding, linking new knowledge to experiences, challenging existing knowledge, and using open-ended questions. The document also discusses Vygotsky's sociocultural theory, including the idea of the zone of proximal development and how children can be encouraged to solve problems beyond their current abilities with help from more expert others. In summary, the document outlines Piaget and Vygotsky's influential theories on cognitive development and how teachers can support students' intellectual growth according to different stages and concepts in these theoriesContributors of Teaching Competency in Student Teachers



Contributors of Teaching Competency in Student Teachersiosrjce
╠²
The present study examined the comparative strength of direct and indirect relationship among the
variables Teaching Competency, Emotional intelligence, Emotional maturity and teaching interest through path
analysis. A hypothesized model for teaching competency is developed with other three variables and Model
fitting is done through IBM SPSS Amos and uses maximum likelihood to calculate all the path coefficients
simultaneously. A path model was developed with emotional intelligence, emotional maturity and teaching
interest as a predictor of teaching competency. All fit indexes indicated the model was an excellent fit to the
data. The model was able to account for 45% of variance of the teaching competency of the student teachersCrt & language theories



Crt & language theoriesXyrille Yves Zaide
╠²
The theories of language acquisition include Chomsky's theory that children are born with an innate language acquisition device, Crystal's theory that acquisition occurs in 5 stages from babbling to expressing opinions, the functional theory that language has experiential and participative meanings, and the interactionist theory that both biological and social factors influence development through interaction. Behaviorism views acquisition as dependent on imitation and reinforcement while the structural view analyzes language as a system of phonological, grammatical, and lexical elements.Secondary school management



Secondary school managementPriyanka Nain
╠²
These slides talk about styles of school management which include Autocratic, Democratic and Laissez Faire Management.The teacher & the learner



The teacher & the learnerXyrille Yves Zaide
╠²
1. The document discusses the roles and responsibilities of teachers throughout history from Jesus and Confucius to modern teachers.
2. It outlines the qualities of an effective teacher including mastery of subject matter, knowledge of students, and having a scientific attitude.
3. The modern teacher faces pressures in educating students on advanced technology while developing their knowledge and skills to understand it. Their role requires holistically developing students.Translator



TranslatorXyrille Yves Zaide
╠²
This document discusses the differences between translators and interpreters. It states that translators convert written material from one language to another, while interpreters convert spoken material simultaneously or consecutively. Translators work with various written materials across different settings, while interpreters work in settings like conferences and meetings, interpreting speech either simultaneously or listening and interpreting segments consecutively. The document also discusses some of the cognitive processes involved in translation and interpretation, noting translators must account for two languages and cultures, while interpreters work in real-time speech conversion.ą▓ąĖčĆčéčāą░ą╗čīąĮą░čÅ čĆąĄą░ą╗čīąĮąŠčüčéčī ąĖ ą│čĆą░ąĮąĖčåčŗ čüą▓ąŠą▒ąŠą┤čŗ čüąŠą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĮąŠą│ąŠ čāčćąĖč鹥ą╗čÅ



ą▓ąĖčĆčéčāą░ą╗čīąĮą░čÅ čĆąĄą░ą╗čīąĮąŠčüčéčī ąĖ ą│čĆą░ąĮąĖčåčŗ čüą▓ąŠą▒ąŠą┤čŗ čüąŠą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĮąŠą│ąŠ čāčćąĖč鹥ą╗čÅLjudmilla Rozhdestvenskaja
╠²
educationą░čĆčé ą╝ą░č鹥ą╝ą░čéąĖą║ą░ ą║ą░ą║ ą╝ąĄčéą░ą┐čĆąĄą┤ą╝ąĄčéąĮčŗą╣ ą┐čĆąŠčĆčŗą▓



ą░čĆčé ą╝ą░č鹥ą╝ą░čéąĖą║ą░ ą║ą░ą║ ą╝ąĄčéą░ą┐čĆąĄą┤ą╝ąĄčéąĮčŗą╣ ą┐čĆąŠčĆčŗą▓Ljudmilla Rozhdestvenskaja
╠²
ART-MATHMore Related Content
Viewers also liked (20)
TeachersŌĆÖ Competences to Meet Teaching Learning Quality 



TeachersŌĆÖ Competences to Meet Teaching Learning Quality Mas Noer
╠²
This presentation talks about what teachers should have to achieve quality teaching and learning process. Standards for teacher competence in educational assessment of student



Standards for teacher competence in educational assessment of studentMichael Recolito
╠²
This document outlines standards for teacher competence in student assessment developed by three educational organizations. It defines standards as principles accepted by relevant professional groups. The standards state that teachers should be skilled in choosing, developing, administering, scoring, and interpreting various assessment methods, using results to inform instructional decisions and grading. Teachers should also be able to communicate results and recognize inappropriate assessment practices. Teaching and Learning of 21st-century Competencies in Schools 



Teaching and Learning of 21st-century Competencies in Schools Benedict Chua
╠²
The document discusses the teaching and learning of 21st century competencies in Singaporean schools. It outlines a framework for 21st century competencies and how they can be taught through the total curriculum, including co-curricular activities and the Programme for Active Learning. It also discusses building teacher capacity to teach these competencies and ensuring alignment between pre-service teacher training and in-service professional development. Moving forward, the focus will be on further equipping teachers to teach 21st century skills to students.Learning evolution



Learning evolutionLjudmilla Rozhdestvenskaja
╠²
ą¤ąŠą┐čŗčéą░ąĄą╝čüčÅ ąŠčüą╝čŗčüą╗ąĖčéčī, ą║ą░ą║ ąĖąĘą╝ąĄąĮąĖą╗ą░čüčī čłą║ąŠą╗čīąĮą░čÅ čāč湥ą▒ąĮą░čÅ čüčĆąĄą┤ą░ ąĘą░ č鹊čé ą┐ąĄčĆąĖąŠą┤, ą║ąŠč鹊čĆčŗą╣ ą╝ąĮąŠą│ąĖąĄ ąĖąĘ čāčćą░čüčéąĮąĖą║ąŠą▓ "ąŠčģą▓ą░čéčŗą▓ą░čÄčé" čüą▓ąŠąĖą╝ čüąŠą▒čüčéą▓ąĄąĮąĮčŗą╝ ąŠą┐čŗč鹊ą╝ - čāčćąĖč鹥ą╗čīčüą║ąĖą╝ ąĖą╗ąĖ čāč湥ąĮąĖč湥čüą║ąĖą╝. ą¤ąĄčĆąĄą┤ ą▓ą░ą╝ąĖ ą┐ąŠą┐čŗčéą║ą░ - čäąĖą║čüąĖčĆąŠą▓ą░čéčī ąĖ ąŠč鹊ą▒čĆą░ąĘąĖčéčī ą▓ čüčģąĄą╝ą░čģ ąĖ ą║ąŠčĆąŠčéą║ąĖčģ č鹥čüčéą░čģ ą▒čŗčüčéčĆąŠ ą╝ąĄąĮčÅčÄčēčāčÄčüčÅ "ą║ą░čĆčéąĖąĮčā čłą║ąŠą╗čīąĮąŠą│ąŠ ą╝ąĖčĆą░". ąĪ ą┐ąŠą╝ąŠčēčīčÄ ą┐čĆąĄąĘąĄąĮčéą░čåąĖąĖ ą┤ą▓ą░ čāčćąĖč鹥ą╗čÅ ą┐ąŠčüčéą░čĆą░ą╗ąĖčüčī ą┐čĆąĄą┤čüčéą░ą▓ąĖčéčī čüą▓ąŠąĄ ą▓ąĖą┤ąĄąĮąĖąĄ 菹▓ąŠą╗čÄčåąĖąĖ čāč湥ą▒ąĮąŠą╣ čüčĆąĄą┤čŗ ąĖ č鹥čģ ąĖąĘą╝ąĄąĮąĄąĮąĖą╣ ą▓ ą╝ąĄč鹊ą┤ąĖą║ą░čģ, ą┐ąŠą┤čģąŠą┤ą░čģ ą║ ąŠą▒čāč湥ąĮąĖčÄ, ąŠčéąĮąŠčłąĄąĮąĖčÅčģ ą▓ąĮčāčéčĆąĖ čāč湥ą▒ąĮąŠą│ąŠ ą┐čĆąŠčåąĄčüčüą░, ą║ąŠč鹊čĆčŗąĄ ą┐čĆąŠąĖčüčģąŠą┤ąĖą╗ąĖ ą▓ čĆą░čüčüą╝ą░čéčĆąĖą▓ą░ąĄą╝čŗą╣ ą┐čĆąŠą╝ąĄąČčāč鹊ą║ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĖ. ąÆąĄčüčī ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĮąŠą╣ ąŠčéčĆąĄąĘąŠą║ čĆą░ąĘą▒ąĖčé ąĮą░ 4 ą╝ąŠą┤ąĄą╗ąĖ-ą┐ąĄčĆąĖąŠą┤ą░, čĆą░ąĘčāą╝ąĄąĄčéčüčÅ, čŹč鹊 čĆą░ąĘą▒ąĖąĄąĮąĖąĄ - ą░ą▓č鹊čĆčüą║ąŠąĄ - ąŠąĮąŠ čāčüą╗ąŠą▓ąĮąŠ ąĖ čüčāą▒čŖąĄą║čéąĖą▓ąĮąŠ! ąÆą░ąČąĮąŠ, čćč鹊 ą▓čüąĄ čŹčéąĖ ą╝ąŠą┤ąĄą╗ąĖ čüąĄą│ąŠą┤ąĮčÅ "čüčāčēąĄčüčéą▓čāčÄčé" ą▓ čüąŠąĘąĮą░ąĮąĖąĖ čāčćąĖč鹥ą╗čÅ ąŠą┤ąĮąŠą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĮąŠ, ąĮą░ą║ą╗ą░ą┤čŗą▓ą░čÅčüčī ą┤čĆčāą│ ąĮą░ ą┤čĆčāą│ą░ ąĖ čćą░čüčéąĖčćąĮąŠ ą┐ąĄčĆąĄą║čĆčŗą▓ą░čÅčüčī, ąĖ čāčćąĖč鹥ą╗čÄ ąĮčāąČąĮąŠ ąĮą░ą╣čéąĖ čüą▓ąŠąĄ ą╝ąĄčüč鹊, čüą░ą╝ąŠąŠą┐čĆąĄą┤ąĄą╗ąĖčéčīčüčÅ, ą▓ ą║ą░ą║ąŠą╣ ą╝ąŠą┤ąĄą╗ąĖ ąŠąĮ čüąĄą▒čÅ ą▓ąĖą┤ąĖčé, ą║ ą║ą░ą║ąĖą╝ ąĖąĘą╝ąĄąĮąĄąĮąĖčÅą╝ ąŠąĮ ą│ąŠč鹊ą▓?
Models of teaching



Models of teachingAileen Asim
╠²
The document discusses various teaching models including information processing models, behavioural models, personal models, and social models.
It provides details on several information processing models such as Atkinson and Shiffrin's model of memory, Gagne's information processing model, and different types of inquiry teaching models. Behavioural models covered include direct instruction, mastery learning, and programmed instruction models. Personal models summarized are non-directive teaching, developing positive self-concepts, and the project model. Lastly, the social model discusses group teaching, cooperative learning, and simulation methods like sociodrama and role-play.
The document provides an overview of key teaching models with the goal of guiding teachers in planning and5th standard of teacher Assessment 



5th standard of teacher Assessment dayo barbie
╠²
This document discusses assessment for teachers. It defines assessment as measuring something numerically to make a judgment. There are different types of assessment including formative, formal, traditional, summative, and informal. The document outlines teacher knowledge around assessment, including using various assessment techniques to evaluate and improve teaching and learning. It provides examples of how to implement assessments using modern technologies and the significance of assessment for helping students improve their skills. Finally, it describes the qualities of a high quality teacher in relation to assessment, such as believing assessment can improve teaching, making lesson plans, assessing students accurately, and making evidence-based decisions.Speaking: Getting attention



Speaking: Getting attentionFerry Pus Pus
╠²
Getting attention perfectly requires respecting others, showing empathy, speaking audibly and clearly with humility. To gain attention, one must care about the message and prepare it well while also caring for those being addressed. Really wanting to communicate well requires being ready to take risks of being attacked, challenged, or ignored, but also risks of being congratulated, promoted or put in charge. The basics of communicating well involve understanding your audience and yourself, rehearsing your message, and knowing how to entrance and hold your audience's attention through your message and presence. Once attention is gained, it must be maintained through consistent expression of who you are in all communications.ąōąĖąĮ ąĪ.ąś. ą¤ąŠą┤ą│ąŠč鹊ą▓ą║ą░ ą╝ą╗ą░ą┤čłąĖčģ čłą║ąŠą╗čīąĮąĖą║ąŠą▓ ą║ ąĖąĮč鹥ą╗ą╗ąĄą║čéčāą░ą╗čīąĮčŗą╝ čüąŠčüčéčÅąĘą░ąĮąĖčÅą╝: ą┐čĆąŠą▒ą╗ąĄ...



ąōąĖąĮ ąĪ.ąś. ą¤ąŠą┤ą│ąŠč鹊ą▓ą║ą░ ą╝ą╗ą░ą┤čłąĖčģ čłą║ąŠą╗čīąĮąĖą║ąŠą▓ ą║ ąĖąĮč鹥ą╗ą╗ąĄą║čéčāą░ą╗čīąĮčŗą╝ čüąŠčüčéčÅąĘą░ąĮąĖčÅą╝: ą┐čĆąŠą▒ą╗ąĄ...ąĪą▓ąĄčéą╗ą░ąĮą░ ąźą░ąĮčīą║ąŠ
╠²
ą£ą░č鹥čĆąĖą░ą╗čŗ IVčĆąĄčüą┐čāą▒ą╗ąĖą║ą░ąĮčüą║ąŠą│ąŠ čĆąŠąČą┤ąĄčüčéą▓ąĄąĮčüą║ąŠą│ąŠ č乥čüčéąĖą▓ą░ą╗čÅ ą┐ąĄą┤ą░ą│ąŠą│ąĖč湥čüą║ąŠą│ąŠ ą╝ą░čüč鹥čĆčüčéą▓ą░ ą┤ą╗čÅ ąĮą░čćą░ą╗čīąĮąŠą╣ čłą║ąŠą╗čŗBridging the theory-practice gap in LIS education: a UCT experiment - Jaya Ra...



Bridging the theory-practice gap in LIS education: a UCT experiment - Jaya Ra...HELIGLIASA
╠²
This document discusses bridging the theory-practice gap in library and information studies (LIS) education through an experiment at the University of Cape Town (UCT). It provides context on the relationship between theory and practice in LIS education. At UCT, the LIS school is organizationally located within UCT Libraries in an effort to better integrate theory and practice. The document evaluates this model and lessons learned, focusing on how UCT Libraries and the LIS school have worked to address the theory-practice gap and prepare LIS graduates for the changing nature of academic libraries.UTPL-METHODOLOGY AND DIDACTIS I-I-BIMESTRE-(OCTUBRE 2011-FEBRERO 2012)



UTPL-METHODOLOGY AND DIDACTIS I-I-BIMESTRE-(OCTUBRE 2011-FEBRERO 2012)Videoconferencias UTPL
╠²
Universidad T├®cnica Particular de Loja
Carrera: Ingl├®s
Docente: Mgs. Orlando Vicente Lizaldez E.
Ciclo: S├®ptimo
Bimestre: Primero
čüąŠąĘą┤ą░ąĮąĖąĄ ą║ą░ą╗ąĄąĮą┤ą░čĆčÅ Google



čüąŠąĘą┤ą░ąĮąĖąĄ ą║ą░ą╗ąĄąĮą┤ą░čĆčÅ GoogleąÆą░ą╗ąĄąĮčéąĖąĮą░ ąĀąŠą╝ą░ąĮąŠą▓ą░
╠²
ąÆ ą┐čĆąĄąĘąĄąĮčéą░čåąĖąĖ ą┐čĆąĄą┤čüčéą░ą▓ą╗ąĄąĮ ą┐čĆąŠčåąĄčüčü čüąŠąĘą┤ą░ąĮąĖčÅ ą║ą░ą╗ąĄąĮą┤ą░čĆčÅ čü ą┐ąŠą╝ąŠčēčīčÄ čüąĄčĆą▓ąĖčüą░ Google CalendarRole of teacher in intellectual development ppt



Role of teacher in intellectual development pptFarooq Mustafa
╠²
This document discusses the role of teachers in intellectual development according to several theories. It covers Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development in children and how it can be applied in the classroom. Key concepts in Piaget's theory include scaffolding, linking new knowledge to experiences, challenging existing knowledge, and using open-ended questions. The document also discusses Vygotsky's sociocultural theory, including the idea of the zone of proximal development and how children can be encouraged to solve problems beyond their current abilities with help from more expert others. In summary, the document outlines Piaget and Vygotsky's influential theories on cognitive development and how teachers can support students' intellectual growth according to different stages and concepts in these theoriesContributors of Teaching Competency in Student Teachers



Contributors of Teaching Competency in Student Teachersiosrjce
╠²
The present study examined the comparative strength of direct and indirect relationship among the
variables Teaching Competency, Emotional intelligence, Emotional maturity and teaching interest through path
analysis. A hypothesized model for teaching competency is developed with other three variables and Model
fitting is done through IBM SPSS Amos and uses maximum likelihood to calculate all the path coefficients
simultaneously. A path model was developed with emotional intelligence, emotional maturity and teaching
interest as a predictor of teaching competency. All fit indexes indicated the model was an excellent fit to the
data. The model was able to account for 45% of variance of the teaching competency of the student teachersCrt & language theories



Crt & language theoriesXyrille Yves Zaide
╠²
The theories of language acquisition include Chomsky's theory that children are born with an innate language acquisition device, Crystal's theory that acquisition occurs in 5 stages from babbling to expressing opinions, the functional theory that language has experiential and participative meanings, and the interactionist theory that both biological and social factors influence development through interaction. Behaviorism views acquisition as dependent on imitation and reinforcement while the structural view analyzes language as a system of phonological, grammatical, and lexical elements.Secondary school management



Secondary school managementPriyanka Nain
╠²
These slides talk about styles of school management which include Autocratic, Democratic and Laissez Faire Management.The teacher & the learner



The teacher & the learnerXyrille Yves Zaide
╠²
1. The document discusses the roles and responsibilities of teachers throughout history from Jesus and Confucius to modern teachers.
2. It outlines the qualities of an effective teacher including mastery of subject matter, knowledge of students, and having a scientific attitude.
3. The modern teacher faces pressures in educating students on advanced technology while developing their knowledge and skills to understand it. Their role requires holistically developing students.Translator



TranslatorXyrille Yves Zaide
╠²
This document discusses the differences between translators and interpreters. It states that translators convert written material from one language to another, while interpreters convert spoken material simultaneously or consecutively. Translators work with various written materials across different settings, while interpreters work in settings like conferences and meetings, interpreting speech either simultaneously or listening and interpreting segments consecutively. The document also discusses some of the cognitive processes involved in translation and interpretation, noting translators must account for two languages and cultures, while interpreters work in real-time speech conversion.ąōąĖąĮ ąĪ.ąś. ą¤ąŠą┤ą│ąŠč鹊ą▓ą║ą░ ą╝ą╗ą░ą┤čłąĖčģ čłą║ąŠą╗čīąĮąĖą║ąŠą▓ ą║ ąĖąĮč鹥ą╗ą╗ąĄą║čéčāą░ą╗čīąĮčŗą╝ čüąŠčüčéčÅąĘą░ąĮąĖčÅą╝: ą┐čĆąŠą▒ą╗ąĄ...



ąōąĖąĮ ąĪ.ąś. ą¤ąŠą┤ą│ąŠč鹊ą▓ą║ą░ ą╝ą╗ą░ą┤čłąĖčģ čłą║ąŠą╗čīąĮąĖą║ąŠą▓ ą║ ąĖąĮč鹥ą╗ą╗ąĄą║čéčāą░ą╗čīąĮčŗą╝ čüąŠčüčéčÅąĘą░ąĮąĖčÅą╝: ą┐čĆąŠą▒ą╗ąĄ...ąĪą▓ąĄčéą╗ą░ąĮą░ ąźą░ąĮčīą║ąŠ
╠²
More from Ljudmilla Rozhdestvenskaja (20)
ą▓ąĖčĆčéčāą░ą╗čīąĮą░čÅ čĆąĄą░ą╗čīąĮąŠčüčéčī ąĖ ą│čĆą░ąĮąĖčåčŗ čüą▓ąŠą▒ąŠą┤čŗ čüąŠą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĮąŠą│ąŠ čāčćąĖč鹥ą╗čÅ



ą▓ąĖčĆčéčāą░ą╗čīąĮą░čÅ čĆąĄą░ą╗čīąĮąŠčüčéčī ąĖ ą│čĆą░ąĮąĖčåčŗ čüą▓ąŠą▒ąŠą┤čŗ čüąŠą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĮąŠą│ąŠ čāčćąĖč鹥ą╗čÅLjudmilla Rozhdestvenskaja
╠²
educationą░čĆčé ą╝ą░č鹥ą╝ą░čéąĖą║ą░ ą║ą░ą║ ą╝ąĄčéą░ą┐čĆąĄą┤ą╝ąĄčéąĮčŗą╣ ą┐čĆąŠčĆčŗą▓



ą░čĆčé ą╝ą░č鹥ą╝ą░čéąĖą║ą░ ą║ą░ą║ ą╝ąĄčéą░ą┐čĆąĄą┤ą╝ąĄčéąĮčŗą╣ ą┐čĆąŠčĆčŗą▓Ljudmilla Rozhdestvenskaja
╠²
ART-MATHGoogle bett 2013, how to use google apps and social media in school



Google bett 2013, how to use google apps and social media in schoolLjudmilla Rozhdestvenskaja
╠²
Using Google Apps and social media in schools can provide benefits like large storage space, authorized access, security, and integration of third party software. However, it also requires setting up additional accounts, dedicating resources to administration, introducing staff to the new platforms, and establishing clear rules for sharing and collaboration. Potential downsides include data loss from human error and the ongoing tasks of cleanup and adapting to interface changes. The presentation provided examples of using Google Docs, Sheets, Sites, Calendar and Photos for classroom lessons, project collaboration, homework tracking, distance learning, and sharing information on school events.ą▓ąŠąĘą╝ąŠąČąĮąŠčüčéąĖ Google apps ąĖąĮč乊čĆą╝ą░čåąĖąŠąĮąĮąŠ-ąŠą▒čĆą░ąĘąŠą▓ą░č鹥ą╗čīąĮąŠą╣ čüčĆąĄą┤čŗ čłą║ąŠą╗čŗ



ą▓ąŠąĘą╝ąŠąČąĮąŠčüčéąĖ Google apps ąĖąĮč乊čĆą╝ą░čåąĖąŠąĮąĮąŠ-ąŠą▒čĆą░ąĘąŠą▓ą░č鹥ą╗čīąĮąŠą╣ čüčĆąĄą┤čŗ čłą║ąŠą╗čŗLjudmilla Rozhdestvenskaja
╠²
Meta2



Meta2Ljudmilla Rozhdestvenskaja
╠²
ąÜą░ą║ ąĖčüą┐ąŠą╗čīąĘąŠą▓ą░čéčī ąĮąŠą▓čŗąĄ ą▓ąĄą▒-ąĖąĮčüčéčĆčāą╝ąĄąĮčéčŗ ą┤ą╗čÅ ą┤ąŠčüčéąĖąČąĄąĮąĖčÅ ą╝ąĄčéą░ą┐čĆąĄą┤ą╝ąĄčéąĮčŗčģ čĆąĄąĘčāą╗čīčéą░č鹊ą▓ ąŠą▒čāč湥ąĮąĖčÅReading n



Reading nLjudmilla Rozhdestvenskaja
╠²
ążčāąĮą║čåąĖąŠąĮą░ą╗čīąĮąŠąĄ čćč鹥ąĮąĖąĄ. ąĪąŠčüčéą░ą▓ą╗čÅąĄą╝ ąĘą░ą┤ą░ąĮąĖčÅ ą║ č鹥ą║čüčéčā.Ulej 2010



Ulej 2010Ljudmilla Rozhdestvenskaja
╠²
Mesitaru/ŌĆ£ąŻąøąĢąÖŌĆ£
Vene ├Ąppekeelega koolide
├Ąpetajate
virtuaalne praktikakogukond
ą▓ąĖčĆčéčāą░ą╗čīąĮą░čÅ čĆąĄą░ą╗čīąĮąŠčüčéčī ąĖ ą│čĆą░ąĮąĖčåčŗ čüą▓ąŠą▒ąŠą┤čŗ čüąŠą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĮąŠą│ąŠ čāčćąĖč鹥ą╗čÅ



ą▓ąĖčĆčéčāą░ą╗čīąĮą░čÅ čĆąĄą░ą╗čīąĮąŠčüčéčī ąĖ ą│čĆą░ąĮąĖčåčŗ čüą▓ąŠą▒ąŠą┤čŗ čüąŠą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĮąŠą│ąŠ čāčćąĖč鹥ą╗čÅLjudmilla Rozhdestvenskaja
╠²
ą░čĆčé ą╝ą░č鹥ą╝ą░čéąĖą║ą░ ą║ą░ą║ ą╝ąĄčéą░ą┐čĆąĄą┤ą╝ąĄčéąĮčŗą╣ ą┐čĆąŠčĆčŗą▓



ą░čĆčé ą╝ą░č鹥ą╝ą░čéąĖą║ą░ ą║ą░ą║ ą╝ąĄčéą░ą┐čĆąĄą┤ą╝ąĄčéąĮčŗą╣ ą┐čĆąŠčĆčŗą▓Ljudmilla Rozhdestvenskaja
╠²
ą▓ąŠąĘą╝ąŠąČąĮąŠčüčéąĖ Google apps ąĖąĮč乊čĆą╝ą░čåąĖąŠąĮąĮąŠ-ąŠą▒čĆą░ąĘąŠą▓ą░č鹥ą╗čīąĮąŠą╣ čüčĆąĄą┤čŗ čłą║ąŠą╗čŗ



ą▓ąŠąĘą╝ąŠąČąĮąŠčüčéąĖ Google apps ąĖąĮč乊čĆą╝ą░čåąĖąŠąĮąĮąŠ-ąŠą▒čĆą░ąĘąŠą▓ą░č鹥ą╗čīąĮąŠą╣ čüčĆąĄą┤čŗ čłą║ąŠą╗čŗLjudmilla Rozhdestvenskaja
╠²
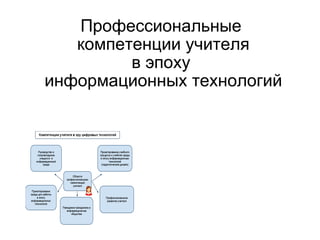
Teacher's competencies
- 1. ą¤čĆąŠč乥čüčüąĖąŠąĮą░ą╗čīąĮčŗąĄ╠² ą║ąŠą╝ą┐ąĄč鹥ąĮčåąĖąĖ╠²čāčćąĖč鹥ą╗čÅ ą▓ 菹┐ąŠčģčā╠² ąĖąĮč乊čĆą╝ą░čåąĖąŠąĮąĮčŗčģ č鹥čģąĮąŠą╗ąŠą│ąĖą╣
- 2. ╠²
- 3. 1 2 3 4 5
- 4. 1
- 5. 2
- 6. 3
- 7. 4
- 8. 5
- 9. ą¤čĆąĖ čüąŠčüčéą░ą▓ą╗ąĄąĮąĖąĖ ą┐čĆąĄąĘąĄąĮčéą░čåąĖąĖ ąĖčüą┐ąŠą╗čīąĘąŠą▓ą░ąĮčŗ ą╝ą░č鹥čĆąĖą░ą╗čŗ╠² ą¤čĆąĄąĘąĄąĮčéą░čåąĖąĖ ą£ą░čĆčéą░ ąøą░ą░ąĮą┐ąĄčĆąĄ╠² Haridustehnoloogilised p├żdevused ą¤ąĄčĆąĄą▓ąĄą╗ą░ čü čŹčüč鹊ąĮčüą║ąŠą│ąŠ ąø.ąĀąŠąČą┤ąĄčüčéą▓ąĄąĮčüą║ą░čÅ


















