2 Defination _Propoties_Units of fluid mechanics.pptx
- 1. FLUID MECHANICS-1 Md. Shariful Islam Phone : 01717196560 Email: shariful.islam@mte.wub.edu.bd
- 4. 4 INTRODUCTION & FLUID DEFINITION ’ü▒ Fluid Mechanics It is a subject which deals with the conditions under which a fluid can remain at rest or in motion. Fluid Mechanics Fluid Statics Fluid Kinematics Fluid Dynamics
- 5. 5 INTRODUCTION & FLUID DEFINITION ’ü▒ FLUID STATICS: It deals with fluid at rest. ’ü▒ FLUID KINEMATICS: It deals with pure motion of fluids without any reference to pressure or any such agents influencing the motion. ’ü▒ FLUID DYNAMICS: It deals with the motion of fluids as a consequence of the pressure and such agent on the fluid
- 6. 6 FLUID MECHANICS ’ü▒ Application Areas of Fluid Mechanics ’é¦ Blood Circulation ’é¦ Cars, Boats, Aircrafts etc. ’é¦ Wind turbine, Power plant, Industrial application ’é¦ Piping and Plumbing
- 9. 9 INTRODUCTION & FLUID DEFINITION ’ü▒ A fluid is a substance which offers no resistance to shear deformation and will continue to deform when subjected to shear stress. ’ü▒ A fluid has no definite shape, and it takes the shape of the container in which it is contained. A shearing force on a fluid will change its shape
- 10. 10 INTRODUCTION & FLUID DEFINITION ’ü▒ From the point of view of fluid mechanics, all matter consists of only two states, fluid and solid. ’ü▒ The technical distinction lies with the reaction of the two to an applied shear or tangential stress. ’ü▒ A solid can resist a shear stress by a static deformation; a fluid cannot. ’ü▒ Any shear stress applied to a fluid, no matter how small, will result in motion of that fluid. ’ü▒ Therefore , the fluid moves and deforms continuously as long as the shear stress is applied.
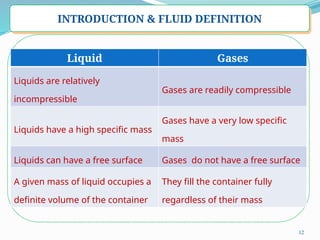
- 11. 11 INTRODUCTION & FLUID DEFINITION ’ü▒ A fluid at rest must be in a state of zero shear stress which is known as the hydrostatic stress condition in structural analysis ’ü▒ Two classes of fluids (a) Liquids and (b) Gases ’ü▒ Under compression all fluids diminish their volume, but reduction in volume is so small in the case of liquids compare to gas therefore ’ü▒ Liquid may be considered to be incompressible fluid and gases are readily compressible
- 12. 12 INTRODUCTION & FLUID DEFINITION Liquid Gases Liquids are relatively incompressible Gases are readily compressible Liquids have a high specific mass Gases have a very low specific mass Liquids can have a free surface Gases do not have a free surface A given mass of liquid occupies a definite volume of the container They fill the container fully regardless of their mass
- 13. 13 PERFECT & ACTUAL FLUID ’ü▒ PERFECT FLUID : It is fluid in which only pressure forces exit whether the fluid is at rest or in motion. In the ideal fluid the internal forces on any internal section are entirely normal to the section even when fluid in motion. Since no tangential force exist, so it is absolutely frictionless. ’ü▒ ACTUAL FLUID: The pressure forces, shearing stress occur when the fluid is in motion.
- 14. 14 FLUID MECHANICS ’ü▒ No Slip Condition: A fluid in direct contact with a solid ŌĆ£SticksŌĆØ to the surface and there is no slip. This is known as the No ŌĆō slip Condition.
- 15. 15 FLUID FLOW (CLASSIFICATION) Fluid mechanics as the science that deals with the behavior of fluids at rest or in motion, and the interaction of fluids with solids or other fluids at the boundaries ’ü▒ Viscous versus inviscid regions of flow ’ü▒ Internal versus external flow ’ü▒ Compressible versus incompressible flow ’ü▒ Laminar versus turbulent flow ’ü▒ Natural versus forced flow ’ü▒ Steady versus unsteady flow ’ü▒ One , two and three dimensional flow
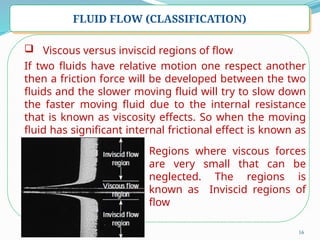
- 16. 16 FLUID FLOW (CLASSIFICATION) ’ü▒ Viscous versus inviscid regions of flow If two fluids have relative motion one respect another then a friction force will be developed between the two fluids and the slower moving fluid will try to slow down the faster moving fluid due to the internal resistance that is known as viscosity effects. So when the moving fluid has significant internal frictional effect is known as viscous fluid Regions where viscous forces are very small that can be neglected. The regions is known as Inviscid regions of flow
- 17. 17 FLUID FLOW (CLASSIFICATION) ’ü▒ Internal versus external flow ’ü▒ Compressible versus incompressible flow ’ü▒ Laminar versus turbulent flow ’ü▒ Natural versus forced flow ’ü▒ Steady versus unsteady flow ’ü▒ One , two and three dimensional flow
- 18. 18 FLUID PROPERTIES ’ü▒ Density or Specific mass (Žü): Mass of fluid per unit volume. ’ü▒ Specific Weight (): Weight of the fluid per unit volume ’ü▒ Relation between specific mass and specific weight is ’ü▒ Specific Volume: Volume of the liquid per unit weight ’ü▒ Specific Gravity (S): Ratio of Density of substance to the density of reference substance. ’ü▒ Apparent Specific Gravity: Ratio of the weight of a volume of the substance to the weight of an equal volume of the reference substance
- 19. 19 FLUID PROPERTIES Class Room Assignment 1. Calculate the specific weight, density and specific gravity of one litre of a liquid which weighs 7.0N. 2. A liquid has a specific gravity of 0.70. Find its density and specific weight. Find also the weight per litre of the liquid. 3. A reservoir of glycerin has a mass of 1200 kg and a volume of 0.952 m3. Find the glycerin weight, density, specific weight and specific gravity 4. A body requires a force of 100 N to accelerate it at a rate of 20 m/s2 . Determine the mass of the body in kg.
- 20. Thanks You