Conduction_Analysis_Dimensional_Analysis_and_Fin_Design.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes8 views
The document provides an overview of heat conduction, emphasizing its definition as the transfer of heat through a material without physical movement. It discusses the significance of dimensional analysis in simplifying physical relationships and presents Fourier's law of heat conduction to explain heat flux and thermal conductivity. The content covers essential concepts relevant to conduction analysis and fin design in mechanical engineering.
1 of 3
Download to read offline


More Related Content
More from MdHelalHossain6 (20)
Recently uploaded (20)
PDF
MODULE-5 notes [BCG402-CG&V] PART-B.pdfAlvas Institute of Engineering and technology, MoodabidriĚý
PDF
Decision support system in machine learning models for a face recognition-bas...TELKOMNIKA JOURNALĚý
Decision support system in machine learning models for a face recognition-bas...TELKOMNIKA JOURNAL
Ěý
Ad
Conduction_Analysis_Dimensional_Analysis_and_Fin_Design.pptx
- 1. Conduction Analysis, Dimensional Analysis, and Fin Design A Comprehensive Overview Md. Helal Hossain World University of Bangladesh, Department of Mechanical Engineering
- 2. Introduction • Overview of Heat Conduction • - Heat conduction is the transfer of heat through a material without the movement of the material itself. • Importance of Dimensional Analysis • - Dimensional analysis helps in simplifying physical relationships by reducing the number of variables.
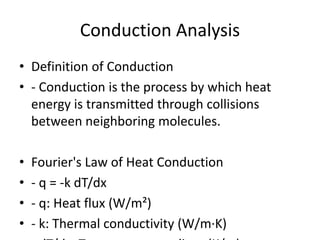
- 3. Conduction Analysis • Definition of Conduction • - Conduction is the process by which heat energy is transmitted through collisions between neighboring molecules. • Fourier's Law of Heat Conduction • - q = -k dT/dx • - q: Heat flux (W/m²) • - k: Thermal conductivity (W/m·K)