Proteinsynthesis
Download as PPTX, PDF1 like304 views
Protein synthesis involves two main steps: transcription and translation. In transcription, RNA polymerase uses DNA as a template to make mRNA strands in the nucleus. The mRNA then moves to the cytoplasm. In translation, ribosomes read the mRNA and join amino acids specified by codons through attachment to tRNAs. The amino acids bond together into a protein chain that eventually folds into its functional tertiary structure.
1 of 33
Download to read offline

Recommended
BWoodrow Protein Synthesis Flip Book 



BWoodrow Protein Synthesis Flip Book punxsyscience
Ěý
The document summarizes the two main processes of protein synthesis: transcription and translation. During transcription, RNA polymerase in the nucleus copies DNA into a messenger RNA strand. During translation, the mRNA strand exits the nucleus and attaches to a ribosome in the cytoplasm. The ribosome then reads the mRNA codons and links amino acids together to form a polypeptide chain according to the mRNA sequence. This polypeptide chain will later fold into the final protein structure.Protein.synthesis.flipbook



Protein.synthesis.flipbookpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document outlines the process of protein synthesis. First, RNA polymerase transcribes DNA in the nucleus to produce mRNA. The mRNA exits the nucleus and binds to ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Ribosomes then translate the mRNA by linking amino acids specified by codons until reaching a stop codon, forming a polypeptide chain. The polypeptide chain folds into its final three-dimensional protein structure.Protein.synthesis.flipbook



Protein.synthesis.flipbookpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document outlines the process of protein synthesis. First, RNA polymerase transcribes DNA in the nucleus to produce mRNA. The mRNA exits the nucleus and binds to ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Ribosomes then translate the mRNA by matching tRNA anticodons to mRNA codons, linking amino acids together to form a polypeptide chain. Translation continues until a stop codon is reached, and the final polypeptide folds into its tertiary structure.Protein.synthesis.flipbook



Protein.synthesis.flipbookpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document outlines the process of protein synthesis. First, RNA polymerase transcribes DNA in the nucleus to produce mRNA. The mRNA exits the nucleus and binds to ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Ribosomes then translate the mRNA into a polypeptide chain as tRNA brings amino acids to pair with mRNA codons. The process continues until a stop codon is reached, resulting in a folded protein with tertiary structure.Kshoemaker Protein synthesis project



Kshoemaker Protein synthesis projectpunxsyscience
Ěý
DNA is transcribed into mRNA in the nucleus. The mRNA is then transported to the cytoplasm where it undergoes translation using ribosomes. During translation, tRNA molecules matching the mRNA codons bring amino acids to the ribosome where they are linked together into a polypeptide chain. The process continues until a stop codon is reached, resulting in a complete protein.BiologyExchange.co.uk Shared Resource



BiologyExchange.co.uk Shared Resourcebiologyexchange
Ěý
The document discusses protein synthesis which begins with DNA carrying the code for amino acid sequences. During transcription, a copy of the DNA sequence is made into messenger RNA (mRNA) which then leaves the nucleus. During translation, transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome based on complementary base pairing between the tRNA anticodon and mRNA codons. Amino acids are joined by peptide bonds to form the polypeptide chain.Protein synthesisDevonDubensky



Protein synthesisDevonDubenskypunxsyscience
Ěý
The process of transcription begins in the cell nucleus, where RNA polymerase breaks apart DNA and uses it as a template to create mRNA strands. During this process, thymine is replaced with uracil to form RNA. The mRNA strand then exits the nucleus through a nuclear pore. Translation occurs in the cytoplasm, where the mRNA is read by ribosomes in groups of three codons. Transfer RNA molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome based on codon-anticodon base pairing. As the ribosome moves along the mRNA, the growing polypeptide chain is released once a stop codon is reached.ProteinSynthesisbyoung



ProteinSynthesisbyoungpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document describes the two-stage process of protein synthesis: transcription and translation. In transcription, RNA polymerase copies DNA in the nucleus to produce mRNA. Translation then occurs in the cytoplasm, where ribosomes read the mRNA to assemble amino acids into a protein chain according to the mRNA's codons. Through this two-step process, the genetic code stored in DNA is used to synthesize functional proteins.Protein.synthesis.flipbook



Protein.synthesis.flipbookpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document describes the process of protein synthesis. It shows RNA polymerase transcribing DNA in the nucleus to produce mRNA. The mRNA exits the nucleus through nuclear pores and binds to ribosomes in the cytoplasm. The ribosomes then translate the mRNA into a polypeptide chain as tRNA molecules add amino acids specified by mRNA codons. This process continues until a stop codon is reached, resulting in a completed protein that folds into its tertiary structure.Dkelly protein sythesis 



Dkelly protein sythesis punxsyscience
Ěý
Protein synthesis begins with the transcription of DNA into mRNA within the nucleus. RNA polymerase separates the DNA strands and copies the coding region of DNA into a mRNA strand until reaching the termination sequence. The mRNA strand then exits the nucleus and binds to a ribosome in the cytoplasm. Transfer RNA molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome according to the mRNA codons. The amino acids are linked together through peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain until a stop codon is reached. The polypeptide chain folds into its tertiary structure to become a functional protein.Sec. 4 the dna connection



Sec. 4 the dna connectionHamdy Karim
Ěý
The document describes the process of protein synthesis through translation of messenger RNA (mRNA) in three steps: 1) A ribosome attaches to an mRNA molecule and brings an amino acid that binds to the first codon on the mRNA. 2) A transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule arrives with a matching anticodon that binds to the codon, and another tRNA brings a second amino acid. 3) The two amino acids form a peptide bond, and the ribosome moves along the mRNA, repeating the process until a stop codon is reached and a full polypeptide is synthesized.Translation flipbook



Translation flipbookpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document summarizes the process of protein synthesis in 3 steps: (1) Transcription of DNA into mRNA in the nucleus, (2) Export of mRNA from the nucleus into the cytoplasm, (3) Translation of mRNA by ribosomes into a polypeptide chain that folds into a protein.Dr. jekle and mr. hyde protein synthesis



Dr. jekle and mr. hyde protein synthesispunxsyscience
Ěý
The document summarizes the process of protein synthesis in 3 steps: (1) Transcription of DNA into mRNA in the nucleus, (2) Export of mRNA from the nucleus into the cytoplasm, (3) Translation of mRNA by ribosomes into a polypeptide chain that folds into a protein.Translation



TranslationMicrobiology
Ěý
Translation, transcription, and transduction are processes involved in gene expression and DNA transfer. Translation is the process by which messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded by ribosomes to produce a polypeptide. Transcription is the process where DNA is copied into mRNA by RNA polymerase. Transduction is the transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another mediated by bacteriophages through generalized or specialized transduction. These processes play important roles in protein production and genetic exchange.Laken flipbook



Laken flipbookpunxsyscience
Ěý
The protein synthesis process involves two main steps: transcription and translation. During transcription, RNA polymerase binds to DNA and synthesizes mRNA using the DNA as a template. The mRNA then leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm. During translation, ribosomes and tRNA molecules work together to translate the mRNA into a polypeptide chain by linking amino acids in the specified order. The polypeptide then folds into the final tertiary protein structure.Rna and protein synthesis



Rna and protein synthesisWenny Wang Wu
Ěý
RNA plays an essential role in protein synthesis by carrying copies of DNA's instructions from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. There are three main types of RNA: messenger RNA carries copies of genes to ribosomes for protein assembly, ribosomal RNA is a component of ribosomes, and transfer RNA transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis. The process of protein synthesis involves transcription of DNA to mRNA in the nucleus, followed by translation of mRNA's codons into amino acids on ribosomes in the cytoplasm.Mol genet-8. transkripsi2



Mol genet-8. transkripsi2S'Roni Roni
Ěý
The document discusses RNA processing, which involves several key steps:
1) Capping at the 5' end, which protects RNA from degradation and aids in transport and splicing.
2) Polyadenylation at the 3' end, which also protects RNA and aids in transport.
3) Splicing, which removes introns and joins exons using a spliceosome complex.
The end result is mature mRNA that can be translated into protein.Genetic code



Genetic codeIqraSami3
Ěý
The sequence ofĚýnucleotidesĚýinĚýdeoxyribonucleic acidĚý(DNA) andĚýribonucleic acidĚý(RNA) that determines theĚýamino acidĚýsequence of proteins. Though the linear sequence of nucleotides in DNA contains the information forĚýproteinĚýsequences, proteins are not made directly from DNA. Instead, aĚýmessenger RNAĚý(mRNA) molecule is synthesized from the DNA and directs the formation of the protein. RNA is composed of four nucleotides: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), andĚýuracil."(U)." Translation



TranslationSt. Xavier's college, maitighar,Kathmandu
Ěý
Translation is the process by which the genetic code in mRNA is used to direct the synthesis of proteins. It involves three main steps - initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation requires the small and large ribosomal subunits to assemble around an mRNA molecule along with initiator tRNA and other initiation factors. Elongation then adds amino acids one by one to the growing polypeptide chain according to the mRNA codons. Termination occurs when a stop codon is reached, causing the ribosome to dissociate and release the complete protein.RNA



RNACheng Mendoza
Ěý
The document discusses RNA synthesis and mRNA processing in eukaryotes. It describes that mRNA processing begins with transcription by RNA polymerase, which adds a 5' methylated cap. Specific sequences in the pre-mRNA are then bound by cleavage factors, moving the 3' end into the correct configuration for cleavage. Poly A polymerase then binds and cleaves the 3' end, synthesizing an adenine tail, with additional proteins binding to increase tail growth until it reaches full length. The processed mRNA is then ready for splicing before translation.Sint. proteĂnas



Sint. proteĂnasRoma29
Ěý
The document discusses protein synthesis and degradation. Protein synthesis occurs in the rough endoplasmic reticulum through translation - the process of mRNA being converted to protein with the help of tRNA and ribosomes. The translation process involves initiation, elongation, and termination steps. Protein degradation is carried out by the proteasome. Several inhibitors are listed that target different steps in protein synthesis, some affecting bacteria and eukaryotes, while others only affect one domain. Protein folding is also mentioned.General characteristic of genetic code



General characteristic of genetic codeAkshay Wakte
Ěý
presentation explain the general Characteristic of genetic code as well as biological significance of the degeneracy.Genetic code2



Genetic code2primecashTraining
Ěý
The document discusses genetic code, gene expression, and DNA fingerprinting. It first explains that the genetic code is the relationship between mRNA nucleotide sequences and the amino acid sequences in polypeptides. It then notes that in 1954, George Gamow proposed that the genetic code should be made up of three nucleotides to code for all 20 amino acids. Finally, it outlines the three stages of protein synthesis - initiation, elongation, and termination - and provides details on the initiation stage in prokaryotes, including the components required such as the ribosome, mRNA, initiation tRNA, and three initiation factors.protein_synthesis



protein_synthesisJonah Howard
Ěý
The document discusses protein synthesis, which involves DNA providing instructions in the form of mRNA that are read by ribosomes to assemble amino acids in the correct sequence. There are 20 amino acids that make up proteins. The instructions start as DNA and are transcribed into mRNA through base-pair matching, then the mRNA travels to ribosomes where the codon sequences are translated to select the corresponding amino acids using tRNA. Mutations can occur that change the amino acid sequence and prevent proper protein formation.BIOC 2011 TH



BIOC 2011 THJonathan Resch
Ěý
This document discusses Parkinson's disease and its treatment with L-DOPA and carbidopa. Parkinson's is characterized by the death of dopaminergic neurons in the brain, resulting in movement issues from low dopamine levels. L-DOPA is converted to dopamine in the brain by the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase, while carbidopa inhibits tyrosine hydroxylase outside the brain to prevent side effects from excess dopamine elsewhere. The combination treatment localizes the therapeutic effects of dopamine production to the brain.Wobble hypothesis



Wobble hypothesisShashankPatil54
Ěý
The document discusses codon-anticodon interactions and the wobble hypothesis. It explains that tRNAs have anticodons that interact with mRNA codons to add the correct amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain. The wobble hypothesis proposes that the third position of codons and first position of anticodons allow some variability, or "wobbling", in base pairing through interactions with inosine and other modified bases. This wobbling allows a single tRNA to bind to multiple codons, resolving the redundancy in the genetic code and allowing fewer tRNAs than codons.Protien synthesis flip book



Protien synthesis flip bookpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document summarizes the process of protein synthesis in cells. It occurs in two main steps - transcription and translation. In transcription, RNA polymerase in the nucleus copies DNA into mRNA. In translation, ribosomes in the cytoplasm read the mRNA and assemble amino acids into a protein chain using transfer RNA molecules. The end result is a functional protein that forms from the folding and shaping of the amino acid chain.Yoho protein synthesis



Yoho protein synthesispunxsyscience
Ěý
DNA is transcribed into mRNA which is then translated into proteins. Transcription involves RNA polymerase making a complementary mRNA copy of a DNA gene. Translation occurs when ribosomes read the mRNA and join amino acids specified by codons until reaching a stop codon, forming a polypeptide chain that folds into a functional protein. tRNA molecules carry amino acids to the ribosome and recognize codons via complementary anticodons.please explain transcription and translationSolutionAnsTran.pdf



please explain transcription and translationSolutionAnsTran.pdfsiennatimbok52331
Ěý
please explain transcription and translation
Solution
Ans:
Transcription is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene sequence. This copy, called a
messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule, leaves the cell nucleus and enters the cytoplasm, where it
directs the synthesis of the protein, which it encodes. Translation is the process of translating the
sequence of a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule to a sequence of amino acids during protein
synthesis. The genetic code describes the relationship between the sequence of base pairs in a
gene and the corresponding amino acid sequence that it encodes. In the cell cytoplasm, the
ribosome reads the sequence of the mRNA in groups of three bases to assemble the protein.
Transcription is the process by which DNA is copied (transcribed) to mRNA, which carries the
information needed for protein synthesis. Transcription takes place in two broad steps. First, pre-
messenger RNA is formed, with the involvement of RNA polymerase enzymes. The process
relies on Watson-Crick base pairing, and the resultant single strand of RNA is the reverse-
complement of the original DNA sequence. The pre-messenger RNA is then \"edited\" to
produce the desired mRNA molecule in a process called RNA splicing.
Formation of pre-messenger RNA
The mechanism of transcription has parallels in that of DNA replication. As with DNA
replication, partial unwinding of the double helix must occur before transcription can take place,
and it is the RNA polymerase enzymes that catalyze this process.
Unlike DNA replication, in which both strands are copied, only one strand is transcribed. The
strand that contains the gene is called the sense strand, while the complementary strand is the
antisense strand. The mRNA produced in transcription is a copy of the sense strand, but it is the
antisense strand that is transcribed.
Ribonucleotide triphosphates (NTPs) align along the antisense DNA strand, with Watson-Crick
base pairing (A pairs with U). RNA polymerase joins the ribonucleotides together to form a pre-
messenger RNA molecule that is complementary to a region of the antisense DNA strand.
Transcription ends when the RNA polymerase enzyme reaches a triplet of bases that is read as a
\"stop\" signal. The DNA molecule re-winds to re-form the double helix.
RNA splicing
The pre-messenger RNA thus formed contains introns which are not required for protein
synthesis. The pre-messenger RNA is chopped up to remove the introns and create messenger
RNA (mRNA) in a process called RNA splicing
Alternative splicing
In alternative splicing, individual exons are either spliced or included, giving rise to several
different possible mRNA products. Each mRNA product codes for a different protein isoform;
these protein isoforms differ in their peptide sequence and therefore their biological activity. It is
estimated that up to 60% of human gene products undergo alternative splicing.
Alternative splicing contributes to protein diversity a single gene transcript (RNA) can have
tho.Translation , Transcription and Transduction



Translation , Transcription and TransductionMicrobiology
Ěý
Translation is the process by which messenger RNA (mRNA) is used to produce proteins. It occurs in three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. During initiation, the ribosome assembles on the mRNA. In elongation, transfer RNAs (tRNAs) bring amino acids to the ribosome according to the mRNA codons, linking the amino acids into a polypeptide chain. In termination, a stop codon signals the ribosome to release the full protein. Translation allows genes encoded in DNA to be expressed as functional proteins through reading of mRNA templates.More Related Content
What's hot (18)
Protein.synthesis.flipbook



Protein.synthesis.flipbookpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document describes the process of protein synthesis. It shows RNA polymerase transcribing DNA in the nucleus to produce mRNA. The mRNA exits the nucleus through nuclear pores and binds to ribosomes in the cytoplasm. The ribosomes then translate the mRNA into a polypeptide chain as tRNA molecules add amino acids specified by mRNA codons. This process continues until a stop codon is reached, resulting in a completed protein that folds into its tertiary structure.Dkelly protein sythesis 



Dkelly protein sythesis punxsyscience
Ěý
Protein synthesis begins with the transcription of DNA into mRNA within the nucleus. RNA polymerase separates the DNA strands and copies the coding region of DNA into a mRNA strand until reaching the termination sequence. The mRNA strand then exits the nucleus and binds to a ribosome in the cytoplasm. Transfer RNA molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome according to the mRNA codons. The amino acids are linked together through peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain until a stop codon is reached. The polypeptide chain folds into its tertiary structure to become a functional protein.Sec. 4 the dna connection



Sec. 4 the dna connectionHamdy Karim
Ěý
The document describes the process of protein synthesis through translation of messenger RNA (mRNA) in three steps: 1) A ribosome attaches to an mRNA molecule and brings an amino acid that binds to the first codon on the mRNA. 2) A transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule arrives with a matching anticodon that binds to the codon, and another tRNA brings a second amino acid. 3) The two amino acids form a peptide bond, and the ribosome moves along the mRNA, repeating the process until a stop codon is reached and a full polypeptide is synthesized.Translation flipbook



Translation flipbookpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document summarizes the process of protein synthesis in 3 steps: (1) Transcription of DNA into mRNA in the nucleus, (2) Export of mRNA from the nucleus into the cytoplasm, (3) Translation of mRNA by ribosomes into a polypeptide chain that folds into a protein.Dr. jekle and mr. hyde protein synthesis



Dr. jekle and mr. hyde protein synthesispunxsyscience
Ěý
The document summarizes the process of protein synthesis in 3 steps: (1) Transcription of DNA into mRNA in the nucleus, (2) Export of mRNA from the nucleus into the cytoplasm, (3) Translation of mRNA by ribosomes into a polypeptide chain that folds into a protein.Translation



TranslationMicrobiology
Ěý
Translation, transcription, and transduction are processes involved in gene expression and DNA transfer. Translation is the process by which messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded by ribosomes to produce a polypeptide. Transcription is the process where DNA is copied into mRNA by RNA polymerase. Transduction is the transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another mediated by bacteriophages through generalized or specialized transduction. These processes play important roles in protein production and genetic exchange.Laken flipbook



Laken flipbookpunxsyscience
Ěý
The protein synthesis process involves two main steps: transcription and translation. During transcription, RNA polymerase binds to DNA and synthesizes mRNA using the DNA as a template. The mRNA then leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm. During translation, ribosomes and tRNA molecules work together to translate the mRNA into a polypeptide chain by linking amino acids in the specified order. The polypeptide then folds into the final tertiary protein structure.Rna and protein synthesis



Rna and protein synthesisWenny Wang Wu
Ěý
RNA plays an essential role in protein synthesis by carrying copies of DNA's instructions from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. There are three main types of RNA: messenger RNA carries copies of genes to ribosomes for protein assembly, ribosomal RNA is a component of ribosomes, and transfer RNA transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis. The process of protein synthesis involves transcription of DNA to mRNA in the nucleus, followed by translation of mRNA's codons into amino acids on ribosomes in the cytoplasm.Mol genet-8. transkripsi2



Mol genet-8. transkripsi2S'Roni Roni
Ěý
The document discusses RNA processing, which involves several key steps:
1) Capping at the 5' end, which protects RNA from degradation and aids in transport and splicing.
2) Polyadenylation at the 3' end, which also protects RNA and aids in transport.
3) Splicing, which removes introns and joins exons using a spliceosome complex.
The end result is mature mRNA that can be translated into protein.Genetic code



Genetic codeIqraSami3
Ěý
The sequence ofĚýnucleotidesĚýinĚýdeoxyribonucleic acidĚý(DNA) andĚýribonucleic acidĚý(RNA) that determines theĚýamino acidĚýsequence of proteins. Though the linear sequence of nucleotides in DNA contains the information forĚýproteinĚýsequences, proteins are not made directly from DNA. Instead, aĚýmessenger RNAĚý(mRNA) molecule is synthesized from the DNA and directs the formation of the protein. RNA is composed of four nucleotides: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), andĚýuracil."(U)." Translation



TranslationSt. Xavier's college, maitighar,Kathmandu
Ěý
Translation is the process by which the genetic code in mRNA is used to direct the synthesis of proteins. It involves three main steps - initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation requires the small and large ribosomal subunits to assemble around an mRNA molecule along with initiator tRNA and other initiation factors. Elongation then adds amino acids one by one to the growing polypeptide chain according to the mRNA codons. Termination occurs when a stop codon is reached, causing the ribosome to dissociate and release the complete protein.RNA



RNACheng Mendoza
Ěý
The document discusses RNA synthesis and mRNA processing in eukaryotes. It describes that mRNA processing begins with transcription by RNA polymerase, which adds a 5' methylated cap. Specific sequences in the pre-mRNA are then bound by cleavage factors, moving the 3' end into the correct configuration for cleavage. Poly A polymerase then binds and cleaves the 3' end, synthesizing an adenine tail, with additional proteins binding to increase tail growth until it reaches full length. The processed mRNA is then ready for splicing before translation.Sint. proteĂnas



Sint. proteĂnasRoma29
Ěý
The document discusses protein synthesis and degradation. Protein synthesis occurs in the rough endoplasmic reticulum through translation - the process of mRNA being converted to protein with the help of tRNA and ribosomes. The translation process involves initiation, elongation, and termination steps. Protein degradation is carried out by the proteasome. Several inhibitors are listed that target different steps in protein synthesis, some affecting bacteria and eukaryotes, while others only affect one domain. Protein folding is also mentioned.General characteristic of genetic code



General characteristic of genetic codeAkshay Wakte
Ěý
presentation explain the general Characteristic of genetic code as well as biological significance of the degeneracy.Genetic code2



Genetic code2primecashTraining
Ěý
The document discusses genetic code, gene expression, and DNA fingerprinting. It first explains that the genetic code is the relationship between mRNA nucleotide sequences and the amino acid sequences in polypeptides. It then notes that in 1954, George Gamow proposed that the genetic code should be made up of three nucleotides to code for all 20 amino acids. Finally, it outlines the three stages of protein synthesis - initiation, elongation, and termination - and provides details on the initiation stage in prokaryotes, including the components required such as the ribosome, mRNA, initiation tRNA, and three initiation factors.protein_synthesis



protein_synthesisJonah Howard
Ěý
The document discusses protein synthesis, which involves DNA providing instructions in the form of mRNA that are read by ribosomes to assemble amino acids in the correct sequence. There are 20 amino acids that make up proteins. The instructions start as DNA and are transcribed into mRNA through base-pair matching, then the mRNA travels to ribosomes where the codon sequences are translated to select the corresponding amino acids using tRNA. Mutations can occur that change the amino acid sequence and prevent proper protein formation.BIOC 2011 TH



BIOC 2011 THJonathan Resch
Ěý
This document discusses Parkinson's disease and its treatment with L-DOPA and carbidopa. Parkinson's is characterized by the death of dopaminergic neurons in the brain, resulting in movement issues from low dopamine levels. L-DOPA is converted to dopamine in the brain by the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase, while carbidopa inhibits tyrosine hydroxylase outside the brain to prevent side effects from excess dopamine elsewhere. The combination treatment localizes the therapeutic effects of dopamine production to the brain.Wobble hypothesis



Wobble hypothesisShashankPatil54
Ěý
The document discusses codon-anticodon interactions and the wobble hypothesis. It explains that tRNAs have anticodons that interact with mRNA codons to add the correct amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain. The wobble hypothesis proposes that the third position of codons and first position of anticodons allow some variability, or "wobbling", in base pairing through interactions with inosine and other modified bases. This wobbling allows a single tRNA to bind to multiple codons, resolving the redundancy in the genetic code and allowing fewer tRNAs than codons.Similar to Proteinsynthesis (20)
Protien synthesis flip book



Protien synthesis flip bookpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document summarizes the process of protein synthesis in cells. It occurs in two main steps - transcription and translation. In transcription, RNA polymerase in the nucleus copies DNA into mRNA. In translation, ribosomes in the cytoplasm read the mRNA and assemble amino acids into a protein chain using transfer RNA molecules. The end result is a functional protein that forms from the folding and shaping of the amino acid chain.Yoho protein synthesis



Yoho protein synthesispunxsyscience
Ěý
DNA is transcribed into mRNA which is then translated into proteins. Transcription involves RNA polymerase making a complementary mRNA copy of a DNA gene. Translation occurs when ribosomes read the mRNA and join amino acids specified by codons until reaching a stop codon, forming a polypeptide chain that folds into a functional protein. tRNA molecules carry amino acids to the ribosome and recognize codons via complementary anticodons.please explain transcription and translationSolutionAnsTran.pdf



please explain transcription and translationSolutionAnsTran.pdfsiennatimbok52331
Ěý
please explain transcription and translation
Solution
Ans:
Transcription is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene sequence. This copy, called a
messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule, leaves the cell nucleus and enters the cytoplasm, where it
directs the synthesis of the protein, which it encodes. Translation is the process of translating the
sequence of a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule to a sequence of amino acids during protein
synthesis. The genetic code describes the relationship between the sequence of base pairs in a
gene and the corresponding amino acid sequence that it encodes. In the cell cytoplasm, the
ribosome reads the sequence of the mRNA in groups of three bases to assemble the protein.
Transcription is the process by which DNA is copied (transcribed) to mRNA, which carries the
information needed for protein synthesis. Transcription takes place in two broad steps. First, pre-
messenger RNA is formed, with the involvement of RNA polymerase enzymes. The process
relies on Watson-Crick base pairing, and the resultant single strand of RNA is the reverse-
complement of the original DNA sequence. The pre-messenger RNA is then \"edited\" to
produce the desired mRNA molecule in a process called RNA splicing.
Formation of pre-messenger RNA
The mechanism of transcription has parallels in that of DNA replication. As with DNA
replication, partial unwinding of the double helix must occur before transcription can take place,
and it is the RNA polymerase enzymes that catalyze this process.
Unlike DNA replication, in which both strands are copied, only one strand is transcribed. The
strand that contains the gene is called the sense strand, while the complementary strand is the
antisense strand. The mRNA produced in transcription is a copy of the sense strand, but it is the
antisense strand that is transcribed.
Ribonucleotide triphosphates (NTPs) align along the antisense DNA strand, with Watson-Crick
base pairing (A pairs with U). RNA polymerase joins the ribonucleotides together to form a pre-
messenger RNA molecule that is complementary to a region of the antisense DNA strand.
Transcription ends when the RNA polymerase enzyme reaches a triplet of bases that is read as a
\"stop\" signal. The DNA molecule re-winds to re-form the double helix.
RNA splicing
The pre-messenger RNA thus formed contains introns which are not required for protein
synthesis. The pre-messenger RNA is chopped up to remove the introns and create messenger
RNA (mRNA) in a process called RNA splicing
Alternative splicing
In alternative splicing, individual exons are either spliced or included, giving rise to several
different possible mRNA products. Each mRNA product codes for a different protein isoform;
these protein isoforms differ in their peptide sequence and therefore their biological activity. It is
estimated that up to 60% of human gene products undergo alternative splicing.
Alternative splicing contributes to protein diversity a single gene transcript (RNA) can have
tho.Translation , Transcription and Transduction



Translation , Transcription and TransductionMicrobiology
Ěý
Translation is the process by which messenger RNA (mRNA) is used to produce proteins. It occurs in three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. During initiation, the ribosome assembles on the mRNA. In elongation, transfer RNAs (tRNAs) bring amino acids to the ribosome according to the mRNA codons, linking the amino acids into a polypeptide chain. In termination, a stop codon signals the ribosome to release the full protein. Translation allows genes encoded in DNA to be expressed as functional proteins through reading of mRNA templates.Tfb hanna



Tfb hannapunxsyscience
Ěý
The document describes the processes of transcription and translation. During transcription, RNA polymerase binds to DNA at a promoter region and unzips the DNA strands. It reads the template strand and synthesizes a complementary mRNA strand, replacing thymine with uracil. The DNA then rebonds its strands. The mRNA exits the nucleus through pores into the cytoplasm. During translation, the mRNA binds to ribosomes where transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules match their anticodons to the mRNA codons. This causes amino acids to attach to the growing polypeptide chain.Translation and post translational modifications



Translation and post translational modificationsBASALINGAPPA GUTTEDAR
Ěý
Here I had describing translation and post translational modification in a simple way for under graduates and post graduatesprotein translation



protein translationDr-HAMDAN
Ěý
The document summarizes the process of protein translation, which involves messenger RNA (mRNA) being used as a template to produce a polypeptide chain through the joining of amino acids. Key steps include transcription producing mRNA from DNA, mRNA binding to ribosomes in the cytoplasm, transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules matching codons on mRNA to deliver corresponding amino acids, and the growth of the polypeptide chain through the formation of peptide bonds until a stop codon is reached, terminating translation. The genetic code and roles of various RNAs like rRNA and tRNA in facilitating translation are also outlined.Protein synthesis



Protein synthesisWAYNE FERNANDES
Ěý
The document summarizes the process of protein synthesis which occurs in two main steps - transcription and translation. In transcription, a copy of mRNA is made from DNA in the nucleus. This mRNA copy then moves to the cytoplasm. In translation, the mRNA binds to ribosomes where tRNA molecules add amino acids to form a polypeptide chain based on the mRNA sequence. The polypeptide breaks away once a stop codon is reached on the mRNA, completing protein synthesis.Translation (protein synthesis) presentation



Translation (protein synthesis) presentationsikandarsikandar3
Ěý
This document summarizes the process of protein synthesis through translation. It discusses how mRNA is transcribed from DNA and carries genetic codes to ribosomes. Ribosomes then translate mRNA into a polypeptide chain using transfer RNA (tRNA) and amino acids. The three phases of translation - initiation, elongation, and termination - are described in which mRNA codons are read and amino acids are linked together to form a protein.3.5 transcription & translation



3.5 transcription & translationcartlidge
Ěý
DNA and RNA both contain nucleotides with sugars, bases, and phosphates. DNA contains deoxyribose and thymine, while RNA contains ribose and uracil. DNA exists as two strands, while RNA exists as a single strand. The genetic code uses three-base sequences called codons to specify the twenty amino acids. Transcription produces mRNA from DNA, and translation uses mRNA, tRNA, ribosomes and amino acids to assemble polypeptides specified by mRNA codons. Originally it was believed one gene specified one polypeptide, but exceptions to this rule have been discovered.Proteinsynthesis_ishman



Proteinsynthesis_ishmanpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document summarizes the process of protein synthesis. First, DNA is transcribed in the nucleus to produce mRNA. The mRNA moves to the cytoplasm where it binds to ribosomes. Ribosomes then translate the mRNA into a polypeptide chain by linking amino acids specified by the mRNA codons. Translation continues until a stop codon is reached, resulting in a chain of amino acids that will fold into the final 3D structure of the protein.Protein Synthesis



Protein Synthesisncvpselise
Ěý
The document discusses how genetic information passes from DNA to proteins. It explains that the DNA code is transcribed into mRNA, which is then translated by ribosomes into proteins. During translation, the mRNA codons bind to complementary tRNA anticodons, which bring amino acids. The amino acids are linked together to form a polypeptide chain, which then folds into a functional protein that carries out the genetic trait specified by the DNA.Protein.synthesis.flipbook



Protein.synthesis.flipbookpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document outlines the process of protein synthesis: 1) RNA polymerase transcribes DNA into mRNA in the nucleus; 2) the mRNA exits the nucleus and binds to ribosomes in the cytoplasm; 3) the ribosomes then translate the mRNA into a polypeptide chain as tRNA molecules add amino acids according to the mRNA codons. This process continues until a stop codon is reached, resulting in a functional protein.Molec cellextracredit



Molec cellextracreditbabbileo
Ěý
DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) in the cell nucleus. The mRNA is then transported out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm, where it is translated into a protein with the help of transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomes. Transcription and translation are the two main steps by which the genetic code stored in DNA is used to synthesize proteins according to the DNA instructions.A Presentation on Protein Synthesis for Students



A Presentation on Protein Synthesis for Studentstradersm29
Ěý
Protein Synthesis in Lucid and Easy LanguageTranslation: Protein synthesis



Translation: Protein synthesisDr. Mafatlal Kher
Ěý
Translation is the process by which the genetic code stored in mRNA is used to synthesize proteins. It occurs on ribosomes using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to add amino acids to a growing polypeptide chain. There are three sites on the ribosome - the A site binds incoming tRNA, the P site holds tRNA with the polypeptide chain, and the E site releases tRNA. Through the repetitive binding of tRNA to mRNA codons and formation of peptide bonds, proteins specified by the mRNA are assembled from amino acids based on the genetic code.Translation.pdf



Translation.pdfAsmamawMenelihBelay
Ěý
this document will describes how protein is synthesizing both in prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms during gene expression Flip book



Flip bookpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document describes the process of protein synthesis through transcription and translation. It shows RNA polymerase binding to DNA and transcribing mRNA using the DNA as a template. The mRNA then exits the nucleus through the nuclear pore and binds to a ribosome in the cytoplasm where translation occurs. Amino acids are joined together based on the mRNA codons to form a protein.Protein synthesis



Protein synthesisFiza Khan
Ěý
The document discusses the benefits of exercise for mental health. Regular physical activity can help reduce anxiety and depression and improve mood and cognitive function. Exercise causes chemical changes in the brain that may help protect against mental illness and improve symptoms.iochemisty Translation (protei synthesis)



iochemisty Translation (protei synthesis)Prabesh Raj Jamkatel
Ěý
The document summarizes the process of translation (protein synthesis) from messenger RNA to protein. It describes how mRNA travels from the nucleus to the ribosome in the cytoplasm. The ribosome reads the mRNA codons and uses transfer RNA to add amino acids in the proper sequence specified by the mRNA to produce a protein. Key aspects covered include the genetic code, structure and role of transfer RNA and ribosomes, and the three main stages of translation - initiation, elongation, and termination.More from punxsyscience (20)
Genetics power point



Genetics power pointpunxsyscience
Ěý
Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk who is considered the father of genetics. He conducted experiments with pea plants in which he studied 7 different traits. Through his experiments, Mendel discovered the principles of heredity, including that traits are passed from parents to offspring through discrete units called genes, and that some genes are dominant while others are recessive. When Mendel crossed plants with different traits, he found that the offspring expressed the traits of only one parent, not a blend, and that recessive traits could reappear in later generations. This led Mendel to propose that genes segregate and assort independently during the formation of gametes.Protein synthesis trenton stouffer



Protein synthesis trenton stoufferpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document describes the process of protein synthesis. It explains that RNA polymerase first breaks the hydrogen bonds of DNA to copy it and make an mRNA strand. The mRNA strand then leaves the nucleus through the nuclear pore into the cytoplasm. In the cytoplasm, the mRNA binds to a ribosome where tRNA reads its bases and adds complementary amino acids to form a polypeptide chain.Presentation1



Presentation1punxsyscience
Ěý
Transcription occurs in the cell nucleus where DNA is unzipped and RNA polymerase adds complementary RNA nucleotides to the DNA template strand, forming mRNA. The mRNA is processed - a cap and tail are added and introns are removed. The completed mRNA contains codons of three nucleotides that code for amino acids. Translation occurs in the cytoplasm where the mRNA binds to ribosomes and tRNA molecules with matching anticodons deliver amino acids specified by mRNA codons, assembling the polypeptide chain specified by the mRNA.Atcheson flip book



Atcheson flip bookpunxsyscience
Ěý
This flip book depicts the process of protein synthesis, showing how DNA is transcribed into mRNA, which is then translated by ribosomes into a polypeptide chain. The flip book steps through transcription, where RNA polymerase copies DNA into mRNA, then translation, where the mRNA passes through the ribosome and interacts with tRNA and rRNA to add amino acids in the correct order specified by codons until a full protein is synthesized.Protein synthesis



Protein synthesispunxsyscience
Ěý
This document is a flip book that summarizes the process of protein synthesis. It shows how DNA is transcribed into mRNA by RNA polymerase in the nucleus. The mRNA is then transported out of the nucleus through the nuclear pore and binds to the ribosome in the cytoplasm. The ribosome reads the mRNA codons and binds transfer RNA (tRNA) with complementary anticodons. The tRNA brings amino acids to form peptide bonds and a polypeptide chain, which eventually folds into a functional protein.Protein synthesis



Protein synthesispunxsyscience
Ěý
This flip book depicts the process of protein synthesis, showing how DNA is transcribed into mRNA, which is then translated by ribosomes into a polypeptide chain. The flip book steps through transcription, where RNA polymerase copies DNA into mRNA, then translation, where the mRNA passes through the ribosome and interacts with tRNA and rRNA to add amino acids in the correct order specified by codons until a full protein is synthesized.Protein synthesis project



Protein synthesis projectpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document describes the process of transcription and translation in a cell. RNA polymerase unwinds DNA and creates an mRNA strand in the nucleus. The mRNA strand then moves to the cytoplasm through the nuclear pore. In the cytoplasm, the mRNA strand binds to a ribosome where tRNA brings amino acids to add to a growing polypeptide chain based on the mRNA codons. The polypeptide chain then folds into the final 3D protein structure.Steven detrie protein synthesis model



Steven detrie protein synthesis modelpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document describes the process of protein synthesis, which occurs in two steps: transcription and translation. In transcription, DNA is unwound and an mRNA strand is created using nucleotides. In translation, the mRNA strand is sent to the cytoplasm where it binds to a ribosome. tRNA molecules then bind to the ribosome and add amino acids specified by the mRNA code, forming a peptide bond between amino acids and creating a protein chain.Steven detrie protein synthesis model



Steven detrie protein synthesis modelpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document describes the process of protein synthesis, which occurs in two steps: transcription and translation. In transcription, DNA is unwound and an mRNA strand is created using nucleotides. The mRNA strand is then released and the DNA strands rebind. In translation, the mRNA moves to the cytoplasm and binds to ribosomes. tRNA molecules bind to the ribosome according to the mRNA code, and each tRNA connects to a specific amino acid. Translation begins as tRNA molecules form base pairs with the mRNA, and peptide bonds form between the amino acids, creating a protein.alexis vite flip book



alexis vite flip bookpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document describes the process of protein synthesis, which occurs in two main steps - transcription and translation. Transcription takes place in the nucleus and involves RNA polymerase copying genetic information from DNA to mRNA. Translation occurs in the cytoplasm at ribosomes, where the mRNA code is used to assemble amino acids in the correct order to produce a protein. The start codon on mRNA pairs with a complementary tRNA to initiate translation.Dna replicaton byrd



Dna replicaton byrdpunxsyscience
Ěý
DNA replication begins at the origin of replication where DNA helicase unwinds and unzips the double helix. DNA polymerase reads the bases on one strand and adds complementary bases to the other strand. The leading strand is replicated continuously while the lagging strand is replicated discontinuously in fragments called Okazaki fragments. DNA primase adds primers to fill in the lagging strand, and DNA ligase seals the fragments together with phosphodiester bonds.Mine all mine 



Mine all mine punxsyscience
Ěý
This protein synthesis flip book illustrates the process of transcription and translation. It shows DNA being transcribed into mRNA by RNA polymerase in the nucleus. The mRNA is then transported to the cytoplasm where it passes through ribosomes. During this process, transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules match to the mRNA codons and add amino acids to form a polypeptide chain through peptide bonds. Eventually a full protein is synthesized from the mRNA instructions.RNA_LexiZanaglio



RNA_LexiZanagliopunxsyscience
Ěý
The document outlines the process of protein synthesis which has two main parts - transcription and translation. In transcription, mRNA strands are created in the nucleus from a DNA template with the help of RNA polymerase. The mRNA then exits the nucleus through nuclear pores. In translation, which occurs in the cytoplasm, ribosomes read the mRNA to produce a protein. Transfer RNA molecules match their anticodons to mRNA codons and bring corresponding amino acids. The amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain, which becomes a protein when translation is complete.Protein synthesis flipbook @yoloswagginator24



Protein synthesis flipbook @yoloswagginator24punxsyscience
Ěý
The document summarizes the process of protein synthesis. It describes how RNA polymerase unwinds DNA and copies it to mRNA. The mRNA strand then exits the nucleus through the nuclear pore and moves to ribosomes. At the ribosomes, the mRNA is read and translated to form a polypeptide chain of amino acids.Rna bio



Rna biopunxsyscience
Ěý
The document outlines the process of protein synthesis which has two main parts - transcription and translation. In transcription, mRNA strands are created in the nucleus from a DNA template with the help of RNA polymerase. The mRNA then exits the nucleus through nuclear pores. In translation, which occurs in the cytoplasm, ribosomes read the mRNA to produce a protein. Transfer RNA molecules match their anticodons to mRNA codons and bring corresponding amino acids. The amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain, which becomes a protein when translation is complete.Presentation1



Presentation1punxsyscience
Ěý
The document shows the process of protein synthesis:
1) In the nucleus, RNA polymerase unzips DNA and copies its sequence into a messenger RNA (mRNA) strand.
2) The mRNA exits the nucleus through the nuclear pore and enters the cytoplasm.
3) In the cytoplasm, the mRNA binds to a ribosome which reads its sequence in groups of three bases (codons).
4) Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules matching these codons bring specific amino acids to the ribosome.
5) The amino acids are linked together to form a polypeptide chain, which later folds into a functional protein.Josh.godo protein synthesis 



Josh.godo protein synthesis punxsyscience
Ěý
The document is a flip book that summarizes the key steps of protein synthesis: 1) DNA is unwound in the cell nucleus and an mRNA strand is produced, 2) the mRNA strand moves from the nucleus to the cytoplasm where ribosomes are located, 3) ribosomes read the mRNA strand and amino acids are attached through peptide bonds to form a protein, which then folds into its tertiary structure.Brock flipbook



Brock flipbookpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document summarizes the process of protein synthesis. DNA in the nucleus is transcribed into mRNA by RNA polymerase. The mRNA then exits the nucleus and binds to a ribosome in the cytoplasm. The ribosome reads the mRNA and uses transfer RNA molecules to add amino acids to form a protein chain. The protein folds into its final shape.Jimmy Carrier Protein Synthesis



Jimmy Carrier Protein Synthesispunxsyscience
Ěý
The document discusses protein synthesis in cells. It explains that RNA polymerase in the cell nucleus reads DNA and synthesizes mRNA. The mRNA then exits the nucleus through nuclear pores and binds to ribosomes. At the ribosomes, tRNA matches codons on the mRNA and releases amino acids, forming peptide bonds between amino acids to create a polypeptide chain. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, the polypeptide releases and folds into its tertiary structure to become a functional protein.FlipbookHannahD



FlipbookHannahDpunxsyscience
Ěý
The document summarizes the process of protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells. It explains that mRNA is produced from DNA in the cell nucleus and passes through the nuclear pore into the cytoplasm. Ribosomes then read the mRNA and translate its codon sequence into a chain of amino acids, attaching different tRNAs to each codon. This continues until a stop codon is reached, resulting in a polypeptide that can fold into a functional protein. The key stages are transcription of DNA to mRNA in the nucleus, translation of mRNA to protein by ribosomes in the cytoplasm, and protein folding.Proteinsynthesis
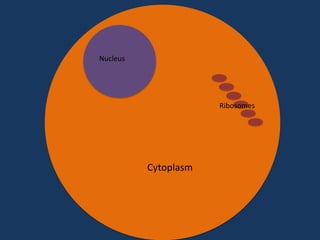
- 1. Protein Synthesis By: Amanda Moore
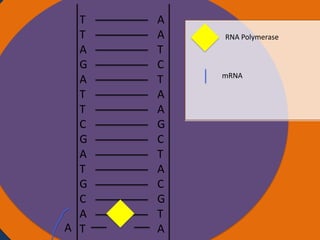
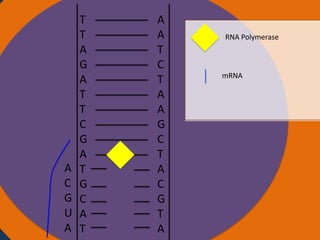
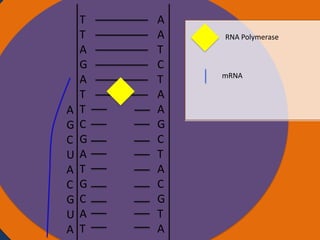
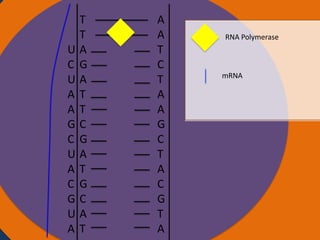
- 6. T T Nucleus A G A T T C G A T G C A A T A A T C T A A G C T A C G T A RNA Polymerase mRNA Ribosomes
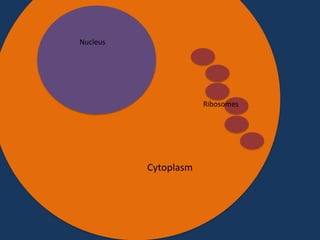
- 7. T T Nucleus A G A T T C G A T G C U A A T A A T C T A A G C T A C G T A RNA Polymerase mRNA Ribosomes
- 8. T T Nucleus A G A T T C G A T G G C U A A T A A T C T A A G C T A C G T A RNA Polymerase mRNA Ribosomes
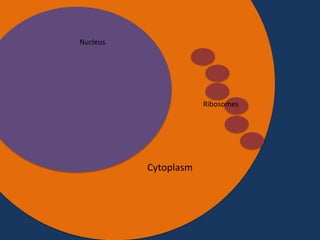
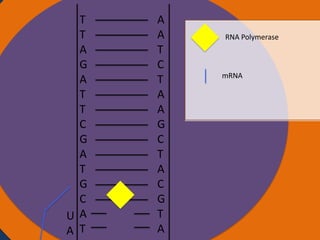
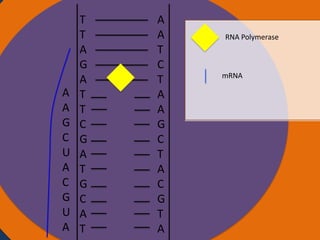
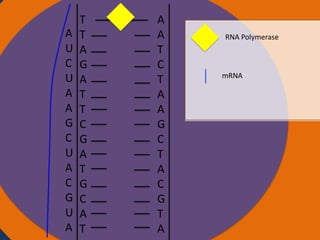
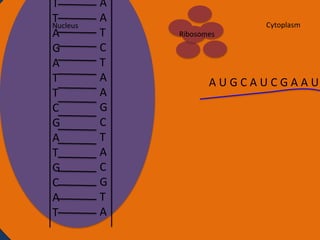
- 22. T T Nucleus A G A T T C G A T G C A T A A T C T A A G C T A C G T A Cytoplasm Ribosomes AUGCAUCGAAU
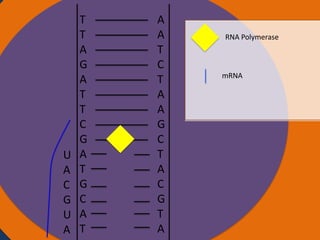
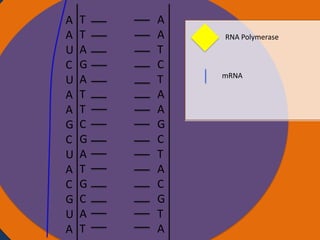
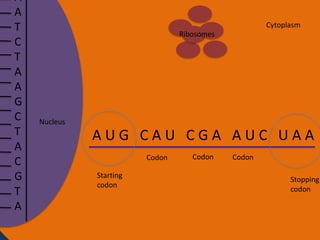
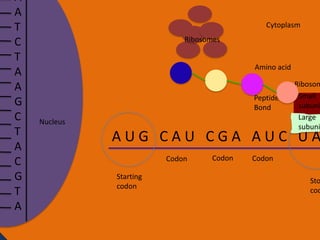
- 23. A A T C T A A G C T A C G T A Cytoplasm Ribosomes Nucleus AUG CAU CGA AUC UAA Codon Starting codon Codon Codon Stopping codon
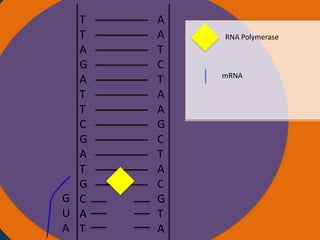
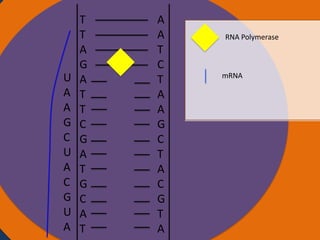
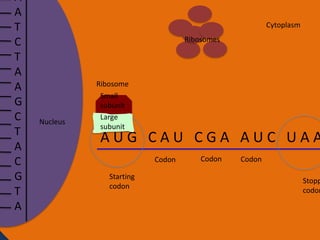
- 24. A A T C T A A G C T A C G T A Cytoplasm Ribosomes Nucleus Ribosome Small subunit Large subunit AUG CAU CGA AUC UAA Codon Starting codon Codon Codon Stopp codon
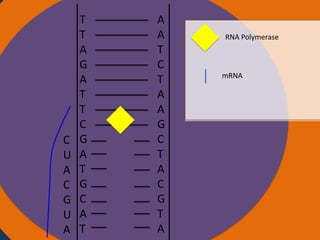
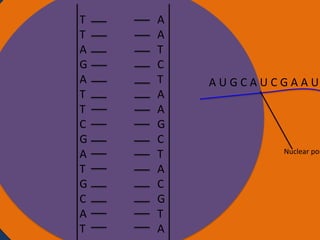
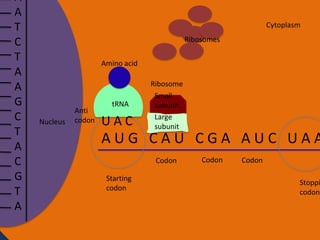
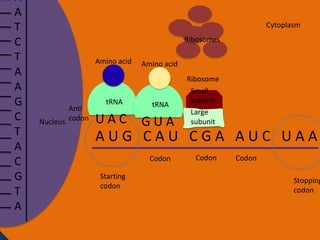
- 25. A A T C T A A G C T A C G T A Cytoplasm Ribosomes Amino acid Nucleus Anti codon tRNA UAC Ribosome Small subunit Large subunit AUG CAU CGA AUC UAA Codon Starting codon Codon Codon Stoppi codon
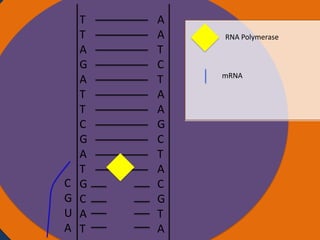
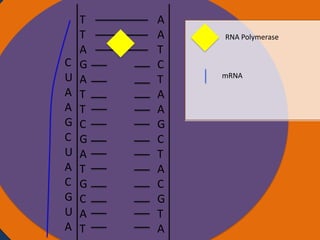
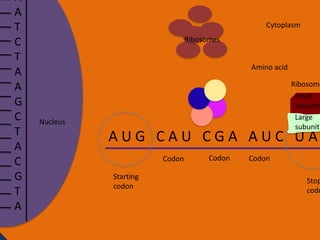
- 26. A A T C T A A G C T A C G T A Cytoplasm Ribosomes Amino acid Anti Nucleus codon tRNA UAC Amino acid tRNA GUA Ribosome Small subunit Large subunit AUG CAU CGA AUC UAA Codon Starting codon Codon Codon Stopping codon
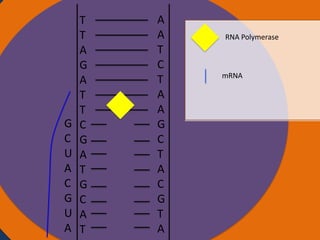
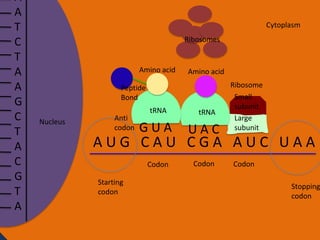
- 27. A A T C T A A G C T A C G T A Cytoplasm Ribosomes Amino acid Amino acid Peptide Bond Nucleus Anti codon tRNA tRNA GUA UAC Codon Codon Ribosome Small subunit Large subunit AUG CAU CGA AUC UAA Starting codon Codon Stopping codon
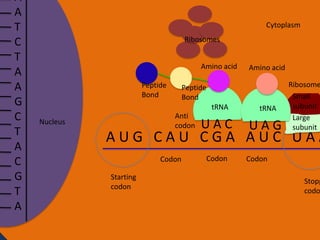
- 28. A A T C T A A G C T A C G T A Cytoplasm Ribosomes Amino acid Peptide Bond Peptide Bond tRNA Anti codon Nucleus Amino acid UAC tRNA UAG Ribosome Small subunit Large subunit AUG CAU CGA AUC UAA Codon Starting codon Codon Codon Stopp codo
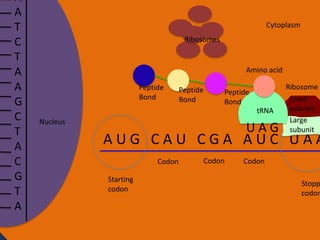
- 29. A A T C T A A G C T A C G T A Cytoplasm Ribosomes Amino acid Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Peptide Bond tRNA Nucleus UAG Ribosome Small subunit Large subunit AUG CAU CGA AUC UAA Codon Starting codon Codon Codon Stopp codon
- 30. A A T C T A A G C T A C G T A Cytoplasm Ribosomes Amino acid Peptide Bond Nucleus Ribosom Small subuni Large subuni AUG CAU CGA AUC UA Codon Starting codon Codon Codon Sto cod
- 31. A A T C T A A G C T A C G T A Cytoplasm Ribosomes Amino acid Ribosome Small subunit Large subunit Nucleus AUG CAU CGA AUC UA Codon Starting codon Codon Codon Stop codo
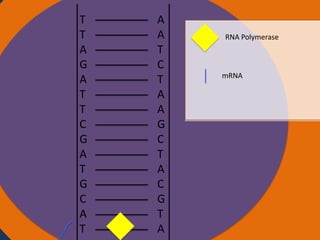
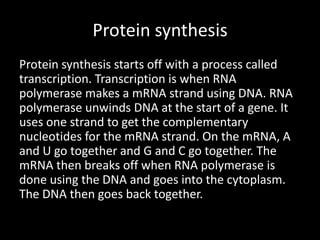
- 32. Protein synthesis Protein synthesis starts off with a process called transcription. Transcription is when RNA polymerase makes a mRNA strand using DNA. RNA polymerase unwinds DNA at the start of a gene. It uses one strand to get the complementary nucleotides for the mRNA strand. On the mRNA, A and U go together and G and C go together. The mRNA then breaks off when RNA polymerase is done using the DNA and goes into the cytoplasm. The DNA then goes back together.
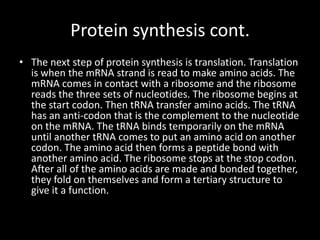
- 33. Protein synthesis cont. • The next step of protein synthesis is translation. Translation is when the mRNA strand is read to make amino acids. The mRNA comes in contact with a ribosome and the ribosome reads the three sets of nucleotides. The ribosome begins at the start codon. Then tRNA transfer amino acids. The tRNA has an anti-codon that is the complement to the nucleotide on the mRNA. The tRNA binds temporarily on the mRNA until another tRNA comes to put an amino acid on another codon. The amino acid then forms a peptide bond with another amino acid. The ribosome stops at the stop codon. After all of the amino acids are made and bonded together, they fold on themselves and form a tertiary structure to give it a function.