x-raydiffraction
1 like72 views
X-ray diffraction is a technique used to analyze the crystal structure of materials. When X-rays strike a crystalline material, they cause the planes of atoms to interfere with one another and produce a distinct diffraction pattern. This pattern can be used like a fingerprint to identify crystalline phases and determine structural properties such as lattice parameters and grain size. X-ray diffraction is a non-destructive technique widely used for applications including phase identification, structural analysis, and thin film measurement. Modern automated X-ray diffractometers have made the technique faster and more accurate.
1 of 27
Download to read offline















Recommended
10. x raydiffraction jntu pharmacy



10. x raydiffraction jntu pharmacyDr. Suman Pattanayak
Ã˝
X-ray diffraction is a technique used to analyze the crystal structure of materials. It works by firing X-rays at a crystalline sample and measuring the angles and intensities of the diffracted X-rays. This diffraction pattern acts as a "fingerprint" identifying the sample. Bragg's law describes how the diffraction pattern relates to the spacing of planes in the crystal lattice. XRD is used to determine properties like lattice parameters, grain size, strain, phase composition and crystal orientation. It has applications in fields like materials science, pharmaceuticals, and forensics.X-Ray Diffraction technique Introduction Working Principal Application.pptx



X-Ray Diffraction technique Introduction Working Principal Application.pptxrishikantmip22
Ã˝
X-Ray DiffractionX ray diffraction(xrd)



X ray diffraction(xrd)kanhaiya kumawat
Ã˝
This document discusses X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques and their application to materials characterization. XRD works on Bragg's law to detect crystalline structures by measuring diffraction patterns from samples bombarded with X-rays. Key applications of XRD include phase identification, crystal structure determination, and measuring properties like crystal size and strain. The document outlines the components of an XRD system and how diffraction data is collected, indexed, and compared to standards to analyze materials. Limitations include issues with non-homogeneous samples and challenges in analyzing complex crystal structures.Xrd mahfooz



Xrd mahfoozMahfooz Alam
Ã˝
The document discusses the principles and techniques of x-ray crystallography, including how x-rays are produced and used to determine crystal structures by measuring diffraction patterns and applying Bragg's law. It also describes how real diffraction patterns may differ from ideal ones due to factors like strain, crystallite size, and instrumentation.Xrd



XrdGITAKRUSHNA
Ã˝
This document summarizes X-ray diffraction (XRD), including what it is, why it is used, common diffraction methods like Bragg's method and powder method, applications like determining crystal structure and lattice constants, and advantages like being inexpensive and convenient while determining crystal structures. The key points covered are that XRD involves X-rays interfering with atomic planes in a crystal, it is used to measure interplanar spacings and determine unknown crystal structures, common methods include Bragg's method using wavelength and angle and powder method using fixed wavelength, and applications involve crystal structure analysis and characterization.X ray diffraction



X ray diffractionsoniaangeline
Ã˝
X-ray diffraction is a technique that uses X-rays to determine the atomic and molecular structure of crystals. When X-rays hit a crystal, they cause the atoms to diffract into specific patterns determined by Bragg's law. By analyzing these diffraction patterns, information about the crystal structure such as lattice parameters and spacing between atomic planes can be determined. Common applications of XRD include identifying materials and determining their purity, structure, and properties.advance material science



advance material scienceMalika Nischal
Ã˝
The Braggs were awarded the Nobel Prize in 1915 for determining crystal structures including NaCl, ZnS, and diamond using X-ray diffraction. Bragg's law describes the angle at which X-rays of a particular wavelength diffract from a crystalline surface as 2dsinθ=nλ, relating inter-plane distance (d), wavelength (λ), diffraction order (n), and scattering angle (θ). Powder X-ray diffraction works by scattering X-rays in a sphere around a sample containing many randomly oriented crystallites, producing a Debye diffraction cone at each Bragg angle.Bm presentation



Bm presentationMalika Nischal
Ã˝
The Braggs were awarded the Nobel Prize in 1915 for determining crystal structures including NaCl, ZnS, and diamond using X-ray diffraction. Bragg's law describes the angle at which X-rays of a particular wavelength diffract from a crystalline surface as 2dsinθ=nλ, relating inter-plane distance (d), wavelength (λ), diffraction order (n), and scattering angle (θ). Powder X-ray diffraction works by scattering X-rays in a sphere around a sample containing many randomly oriented crystallites, producing a Debye diffraction cone at each Bragg angle.x ray diffraction and its application in pharma industry



x ray diffraction and its application in pharma industryNATIONAL INSTITUTE OF PHARMACEUTICAL EDUCATION AND RESEARCH, AHMEDABAD
Ã˝
x ray crystallography and its application in the formulation and development in pharma industries.Xrd



XrdTarun Kumar Reddy
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of x-ray diffraction (XRD) and how it can be used to analyze crystalline materials. It discusses how XRD works based on Bragg's law and diffraction of x-rays by crystal lattice planes. The document also describes how an XRD pattern acts as a "fingerprint" that can be used to identify unknown crystalline phases. Finally, it lists several applications of XRD such as qualitative and quantitative analysis of materials, determining crystal orientations, and measuring properties like crystallite size and thin film thickness.X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRD)



X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRD)Sumit Tiwari
Ã˝
X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) is a technique used to identify crystalline materials by analyzing the scattering pattern of monochromatic X-rays through a powdered sample. XRD works by generating X-rays that interact with the sample, producing constructive interference when conditions satisfy Bragg's law. This diffraction pattern is unique to each mineral and can be used for identification. XRD has various applications including phase identification, determination of unit cell dimensions, and characterization of materials. It provides a rapid and accurate method for mineral identification but requires access to reference patterns for comparison.X ray crystallography 



X ray crystallography ArchanaKR11
Ã˝
X-ray crystallography is a scientific technique used to determine the atomic and molecular structure of crystals. When x-rays strike a crystal, the beam diffracts into specific directions. This diffraction pattern can be analyzed to reveal the nature and structure of the crystal lattice. Bragg's law defines the relationship between x-ray wavelength, diffraction angle, and interplanar spacing and is used to calculate crystal structures from diffraction data. X-ray crystallography is widely used to determine protein structures and has applications in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and other fields.X ray diffraction method



X ray diffraction methodANANT NAG
Ã˝
X-ray diffraction is a technique used to determine the atomic structure of crystals. When X-rays strike the regular array of atoms in a crystal, they produce a pattern of diffracted rays. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, the crystal structure can be analyzed. X-ray crystallography is used across many fields to determine molecular structures, crystal structures, and physical properties of materials. It works by firing X-rays at crystalline samples and observing the diffraction patterns that emerge, which can then be analyzed using Fourier transforms to reveal details about atomic positions and electron densities within the crystal. Common applications of X-ray diffraction include phase identification, structural elucidation of organic and inorganic compounds, andCrystal structure analysis



Crystal structure analysiszoelfalia
Ã˝
This document discusses various techniques for crystal structure analysis using diffraction methods, including X-ray diffraction, electron diffraction, and neutron diffraction. It provides background on the essential physics of Bragg diffraction and scattering. Key topics covered include generating X-rays, basic diffractometer setups, powder and thin film diffraction techniques, and applications such as phase identification and structure determination.XRD- X-Ray diffraction



XRD- X-Ray diffractionBASANTKUMAR123
Ã˝
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) is a technique used to analyze the crystal structure of materials. X-rays are produced when high-energy electrons strike a metal target, and are collimated and passed through a monochromator to produce a narrow beam. When the beam interacts with a crystalline sample, diffraction occurs according to Bragg's law. The diffraction pattern is measured by detectors and analyzed to determine properties such as lattice parameters and crystal structure. Common applications of XRD include identifying crystalline phases, measuring strain, and analyzing thin film materials.XRD principle and application



XRD principle and applicationTechef In
Ã˝
X-ray diffraction is a technique used to analyze the crystal structure of materials. It works by firing x-rays at a crystalline sample and measuring the angles and intensities of the x-rays that are diffracted. The document discusses key concepts like Bragg's law, unit cells, miller indices, and how x-ray diffraction is used to determine properties like phase identification, crystallite size, strain, and lattice parameters. It also outlines the basic components of an x-ray diffractometer and sources of error in measurements.x ray crystallography & diffraction



x ray crystallography & diffractionArman Dalal
Ã˝
X-rays introduction, why xrays, why crystals, Xray diffraction, Bragg's law, Interference, Crystal lattice , Instrumentation of xray crystallography, Production of Xrays, Monochromator, Types of Monochromator, Interference filters, Crystal monochromator, xray diffration methods - single crystal, rotating crystal, powder method, Applications of xray crystallographyX ray Crystallography



X ray Crystallographysilambarasan I
Ã˝
X-ray crystallography uses X-rays to determine the atomic and molecular structure of crystals. When X-rays hit a crystal, they cause the crystalline atoms to diffract the X-rays into specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted X-rays, the crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of electron density within the crystal. From this electron density, the positions of atoms and chemical bonds in the crystal can be determined. There are several methods for X-ray crystallography including Bragg X-ray spectrometry, rotating crystal method, and powder crystal method. X-ray crystallography has many applications including determining crystal and molecular structures, and characterXRD BY SATYAM.pdf



XRD BY SATYAM.pdfSATYAM ASATI
Ã˝
This document discusses X-ray diffraction (XRD), including its principle, concept, instrumentation, methods, and applications. XRD is a technique used for phase identification of crystalline materials based on constructive interference of X-rays diffracted from a crystalline sample. It can provide information on unit cell dimensions. The key components of an XRD instrument are an X-ray tube, sample holder, detector, and analyzer. Common methods include Bragg's method, Laue's method, and powder diffraction. XRD has applications in determining crystal structure, polymer characterization, and particle size analysis.X ray crystallography



X ray crystallographyRajput1998
Ã˝
complete introduction, types of crystal, x-ray production, x-ray diffraction, braggs law, interference, x-ray methods, applications. Xrd



XrdEvi Fitri
Ã˝
X-ray diffraction is a technique used to analyze the crystal structure of materials. It works by firing x-rays at a crystalline sample and measuring the angles and intensities of the x-rays that are diffracted. The diffraction pattern produced can be used to determine properties like unit cell dimensions, bond angles, and phase composition. Bragg's law describes the conditions under which x-ray diffraction occurs from crystalline materials, relating the wavelength, angle of incidence, and interplanar spacing. X-ray diffraction is widely used across many fields including physics, chemistry, materials science, and biology.X ray crystallography



X ray crystallographyMeghaVarshney8
Ã˝
X-ray crystallography uses x-ray diffraction patterns to determine the atomic structure of crystals. X-rays are produced using an x-ray tube and passed through a monochromator to produce a single wavelength. The x-rays are then directed at a crystal sample, which causes the beams to diffract into specific directions based on the crystal structure. Detectors measure the intensities and angles of the diffracted beams, which are used to reconstruct the three-dimensional electron density and atomic positions in the crystal. X-ray crystallography has applications in determining crystal structures, polymer characterization, and analyzing materials.X ray diffraction(xrd) principle and use



X ray diffraction(xrd) principle and useSrikumar Swain
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of X-ray diffraction (XRD). It begins by explaining that XRD is a non-destructive chemical analysis technique that uses X-rays and the atomic structure of crystals to identify substances. Every crystalline substance produces a unique XRD pattern like a fingerprint. The document then discusses how X-rays are generated via electron bombardment, Bragg's law of diffraction, X-ray sources, working principles of XRD, and basic components of an XRD system like the X-ray tube and detector. It also covers sample preparation techniques for clay minerals analysis using XRD.263 4.pdf



263 4.pdfAbitiEthiopia
Ã˝
This document discusses x-ray diffraction techniques and concepts. It begins with an overview of different diffraction techniques including x-ray, electron, and neutron diffraction. Bragg's law of diffraction is then explained, relating the diffraction angle and wavelength to the crystal lattice spacing. Key concepts in x-ray diffraction such as the reciprocal lattice, Laue conditions, and powder vs single crystal diffraction are described. Specific applications and techniques like thin film analysis and Rietveld refinement are also mentioned.263 4.pdf



263 4.pdfJorge Vega Rodríguez
Ã˝
This document discusses various techniques for crystal structure analysis using diffraction of x-rays, electrons, and neutrons. It begins by introducing Bragg diffraction and references several textbooks on topics like x-ray diffraction, small-angle scattering, and protein crystallography. The document then covers the fundamentals of elastic and inelastic scattering, Bragg's law of diffraction, diffraction orders, and applications of techniques like powder diffraction, single-crystal diffraction, and thin film analysis.X ray crystallography for mpharm 



X ray crystallography for mpharm Martin Jacob
Ã˝
X-ray crystallography uses X-ray diffraction patterns to determine the atomic structure of crystals. When X-rays hit a crystal, the electrons cause the X-rays to diffract into specific patterns. By measuring the angles and intensities of the diffracted X-rays, crystallographers can use Fourier transforms to produce a three-dimensional model of electron density within the crystal and determine the positions of atoms and chemical bonds. Researchers must first obtain a sufficiently large, pure, and regularly structured crystal of the material to be studied before collecting X-ray diffraction data and solving the crystal structure.X ray Crystallography



X ray CrystallographyHealth Forager
Ã˝
X ray, invisible, highly penetrating electromagnetic radiation of much shorter wavelength (higher frequency) than visible light. The wavelength range for X rays is from about 10-8 m to about 10-11 m, the corresponding frequency range is from about 3 √ó 1016 Hz to about 3 √ó 1019 Hz.2 Defination _Propoties_Units of fluid mechanics.pptx



2 Defination _Propoties_Units of fluid mechanics.pptxMdHelalHossain6
Ã˝
This is the very fundamental concept of fluid mechanics.More Related Content
Similar to x-raydiffraction (20)
x ray diffraction and its application in pharma industry



x ray diffraction and its application in pharma industryNATIONAL INSTITUTE OF PHARMACEUTICAL EDUCATION AND RESEARCH, AHMEDABAD
Ã˝
x ray crystallography and its application in the formulation and development in pharma industries.Xrd



XrdTarun Kumar Reddy
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of x-ray diffraction (XRD) and how it can be used to analyze crystalline materials. It discusses how XRD works based on Bragg's law and diffraction of x-rays by crystal lattice planes. The document also describes how an XRD pattern acts as a "fingerprint" that can be used to identify unknown crystalline phases. Finally, it lists several applications of XRD such as qualitative and quantitative analysis of materials, determining crystal orientations, and measuring properties like crystallite size and thin film thickness.X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRD)



X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRD)Sumit Tiwari
Ã˝
X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) is a technique used to identify crystalline materials by analyzing the scattering pattern of monochromatic X-rays through a powdered sample. XRD works by generating X-rays that interact with the sample, producing constructive interference when conditions satisfy Bragg's law. This diffraction pattern is unique to each mineral and can be used for identification. XRD has various applications including phase identification, determination of unit cell dimensions, and characterization of materials. It provides a rapid and accurate method for mineral identification but requires access to reference patterns for comparison.X ray crystallography 



X ray crystallography ArchanaKR11
Ã˝
X-ray crystallography is a scientific technique used to determine the atomic and molecular structure of crystals. When x-rays strike a crystal, the beam diffracts into specific directions. This diffraction pattern can be analyzed to reveal the nature and structure of the crystal lattice. Bragg's law defines the relationship between x-ray wavelength, diffraction angle, and interplanar spacing and is used to calculate crystal structures from diffraction data. X-ray crystallography is widely used to determine protein structures and has applications in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and other fields.X ray diffraction method



X ray diffraction methodANANT NAG
Ã˝
X-ray diffraction is a technique used to determine the atomic structure of crystals. When X-rays strike the regular array of atoms in a crystal, they produce a pattern of diffracted rays. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, the crystal structure can be analyzed. X-ray crystallography is used across many fields to determine molecular structures, crystal structures, and physical properties of materials. It works by firing X-rays at crystalline samples and observing the diffraction patterns that emerge, which can then be analyzed using Fourier transforms to reveal details about atomic positions and electron densities within the crystal. Common applications of X-ray diffraction include phase identification, structural elucidation of organic and inorganic compounds, andCrystal structure analysis



Crystal structure analysiszoelfalia
Ã˝
This document discusses various techniques for crystal structure analysis using diffraction methods, including X-ray diffraction, electron diffraction, and neutron diffraction. It provides background on the essential physics of Bragg diffraction and scattering. Key topics covered include generating X-rays, basic diffractometer setups, powder and thin film diffraction techniques, and applications such as phase identification and structure determination.XRD- X-Ray diffraction



XRD- X-Ray diffractionBASANTKUMAR123
Ã˝
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) is a technique used to analyze the crystal structure of materials. X-rays are produced when high-energy electrons strike a metal target, and are collimated and passed through a monochromator to produce a narrow beam. When the beam interacts with a crystalline sample, diffraction occurs according to Bragg's law. The diffraction pattern is measured by detectors and analyzed to determine properties such as lattice parameters and crystal structure. Common applications of XRD include identifying crystalline phases, measuring strain, and analyzing thin film materials.XRD principle and application



XRD principle and applicationTechef In
Ã˝
X-ray diffraction is a technique used to analyze the crystal structure of materials. It works by firing x-rays at a crystalline sample and measuring the angles and intensities of the x-rays that are diffracted. The document discusses key concepts like Bragg's law, unit cells, miller indices, and how x-ray diffraction is used to determine properties like phase identification, crystallite size, strain, and lattice parameters. It also outlines the basic components of an x-ray diffractometer and sources of error in measurements.x ray crystallography & diffraction



x ray crystallography & diffractionArman Dalal
Ã˝
X-rays introduction, why xrays, why crystals, Xray diffraction, Bragg's law, Interference, Crystal lattice , Instrumentation of xray crystallography, Production of Xrays, Monochromator, Types of Monochromator, Interference filters, Crystal monochromator, xray diffration methods - single crystal, rotating crystal, powder method, Applications of xray crystallographyX ray Crystallography



X ray Crystallographysilambarasan I
Ã˝
X-ray crystallography uses X-rays to determine the atomic and molecular structure of crystals. When X-rays hit a crystal, they cause the crystalline atoms to diffract the X-rays into specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted X-rays, the crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of electron density within the crystal. From this electron density, the positions of atoms and chemical bonds in the crystal can be determined. There are several methods for X-ray crystallography including Bragg X-ray spectrometry, rotating crystal method, and powder crystal method. X-ray crystallography has many applications including determining crystal and molecular structures, and characterXRD BY SATYAM.pdf



XRD BY SATYAM.pdfSATYAM ASATI
Ã˝
This document discusses X-ray diffraction (XRD), including its principle, concept, instrumentation, methods, and applications. XRD is a technique used for phase identification of crystalline materials based on constructive interference of X-rays diffracted from a crystalline sample. It can provide information on unit cell dimensions. The key components of an XRD instrument are an X-ray tube, sample holder, detector, and analyzer. Common methods include Bragg's method, Laue's method, and powder diffraction. XRD has applications in determining crystal structure, polymer characterization, and particle size analysis.X ray crystallography



X ray crystallographyRajput1998
Ã˝
complete introduction, types of crystal, x-ray production, x-ray diffraction, braggs law, interference, x-ray methods, applications. Xrd



XrdEvi Fitri
Ã˝
X-ray diffraction is a technique used to analyze the crystal structure of materials. It works by firing x-rays at a crystalline sample and measuring the angles and intensities of the x-rays that are diffracted. The diffraction pattern produced can be used to determine properties like unit cell dimensions, bond angles, and phase composition. Bragg's law describes the conditions under which x-ray diffraction occurs from crystalline materials, relating the wavelength, angle of incidence, and interplanar spacing. X-ray diffraction is widely used across many fields including physics, chemistry, materials science, and biology.X ray crystallography



X ray crystallographyMeghaVarshney8
Ã˝
X-ray crystallography uses x-ray diffraction patterns to determine the atomic structure of crystals. X-rays are produced using an x-ray tube and passed through a monochromator to produce a single wavelength. The x-rays are then directed at a crystal sample, which causes the beams to diffract into specific directions based on the crystal structure. Detectors measure the intensities and angles of the diffracted beams, which are used to reconstruct the three-dimensional electron density and atomic positions in the crystal. X-ray crystallography has applications in determining crystal structures, polymer characterization, and analyzing materials.X ray diffraction(xrd) principle and use



X ray diffraction(xrd) principle and useSrikumar Swain
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of X-ray diffraction (XRD). It begins by explaining that XRD is a non-destructive chemical analysis technique that uses X-rays and the atomic structure of crystals to identify substances. Every crystalline substance produces a unique XRD pattern like a fingerprint. The document then discusses how X-rays are generated via electron bombardment, Bragg's law of diffraction, X-ray sources, working principles of XRD, and basic components of an XRD system like the X-ray tube and detector. It also covers sample preparation techniques for clay minerals analysis using XRD.263 4.pdf



263 4.pdfAbitiEthiopia
Ã˝
This document discusses x-ray diffraction techniques and concepts. It begins with an overview of different diffraction techniques including x-ray, electron, and neutron diffraction. Bragg's law of diffraction is then explained, relating the diffraction angle and wavelength to the crystal lattice spacing. Key concepts in x-ray diffraction such as the reciprocal lattice, Laue conditions, and powder vs single crystal diffraction are described. Specific applications and techniques like thin film analysis and Rietveld refinement are also mentioned.263 4.pdf



263 4.pdfJorge Vega Rodríguez
Ã˝
This document discusses various techniques for crystal structure analysis using diffraction of x-rays, electrons, and neutrons. It begins by introducing Bragg diffraction and references several textbooks on topics like x-ray diffraction, small-angle scattering, and protein crystallography. The document then covers the fundamentals of elastic and inelastic scattering, Bragg's law of diffraction, diffraction orders, and applications of techniques like powder diffraction, single-crystal diffraction, and thin film analysis.X ray crystallography for mpharm 



X ray crystallography for mpharm Martin Jacob
Ã˝
X-ray crystallography uses X-ray diffraction patterns to determine the atomic structure of crystals. When X-rays hit a crystal, the electrons cause the X-rays to diffract into specific patterns. By measuring the angles and intensities of the diffracted X-rays, crystallographers can use Fourier transforms to produce a three-dimensional model of electron density within the crystal and determine the positions of atoms and chemical bonds. Researchers must first obtain a sufficiently large, pure, and regularly structured crystal of the material to be studied before collecting X-ray diffraction data and solving the crystal structure.X ray Crystallography



X ray CrystallographyHealth Forager
Ã˝
X ray, invisible, highly penetrating electromagnetic radiation of much shorter wavelength (higher frequency) than visible light. The wavelength range for X rays is from about 10-8 m to about 10-11 m, the corresponding frequency range is from about 3 √ó 1016 Hz to about 3 √ó 1019 Hz.x ray diffraction and its application in pharma industry



x ray diffraction and its application in pharma industryNATIONAL INSTITUTE OF PHARMACEUTICAL EDUCATION AND RESEARCH, AHMEDABAD
Ã˝
More from MdHelalHossain6 (20)
2 Defination _Propoties_Units of fluid mechanics.pptx



2 Defination _Propoties_Units of fluid mechanics.pptxMdHelalHossain6
Ã˝
This is the very fundamental concept of fluid mechanics.STEAM TURBINE PRESENTATION FOR MECHANICAL ENGINEERS.pdf



STEAM TURBINE PRESENTATION FOR MECHANICAL ENGINEERS.pdfMdHelalHossain6
Ã˝
This is the vital topic for fluid mechanics.35236lect 1Introduction to Masالثالث الثالث مقسم1s Transfer.ppt



35236lect 1Introduction to Masالثالث الثالث مقسم1s Transfer.pptMdHelalHossain6
Ã˝
This slide on mass transfer.ME-4505-2020-Variable-Load-Problems.pptx



ME-4505-2020-Variable-Load-Problems.pptxMdHelalHossain6
Ã˝
This presentation help you understand powerplant engineering.Lecture 03_Metal structure and Crystallization.pptx



Lecture 03_Metal structure and Crystallization.pptxMdHelalHossain6
Ã˝
This slide is crucial for engineering materials.project management -04.ppt



project management -04.pptMdHelalHossain6
Ã˝
Project management involves three key phases: planning, scheduling, and controlling. Planning involves setting objectives, identifying activities, and estimating resources and costs. Scheduling determines the start and finish times of activities using techniques like CPM and PERT to identify the critical path. Controlling monitors progress against the plan and allows for revisions if needed. Effective project management requires thorough planning, scheduling of activities and resources, and ongoing controlling to ensure projects are completed on time and on budget.Hydrogen Production ppt.pptx



Hydrogen Production ppt.pptxMdHelalHossain6
Ã˝
The document discusses several methods for producing hydrogen through water splitting, including:
- Steam reforming of methane, the most common current method.
- Electrolysis, where an electric current splits water into hydrogen and oxygen. More efficient variations include steam electrolysis and thermochemical electrolysis.
- Photochemical and photobiological systems use sunlight to drive the water splitting reaction.
- Thermal water splitting uses very high temperatures of around 1000°C.
- Gasification and biomass conversion also produce hydrogen from other feedstocks.
Low current electrolysis is discussed as a more efficient method, similar to the water splitting that occurs in photosynthesis. Producing hydrogen directly from water without electrolysis is also mentioned. OverallRecently uploaded (20)
Wireless-Charger presentation for seminar .pdf



Wireless-Charger presentation for seminar .pdfAbhinandanMishra30
Ã˝
Wireless technology used in chargerLecture -3 Cold water supply system.pptx



Lecture -3 Cold water supply system.pptxrabiaatif2
Ã˝
The presentation on Cold Water Supply explored the fundamental principles of water distribution in buildings. It covered sources of cold water, including municipal supply, wells, and rainwater harvesting. Key components such as storage tanks, pipes, valves, and pumps were discussed for efficient water delivery. Various distribution systems, including direct and indirect supply methods, were analyzed for residential and commercial applications. The presentation emphasized water quality, pressure regulation, and contamination prevention. Common issues like pipe corrosion, leaks, and pressure drops were addressed along with maintenance strategies. Diagrams and case studies illustrated system layouts and best practices for optimal performance.google_developer_group_ramdeobaba_university_EXPLORE_PPT



google_developer_group_ramdeobaba_university_EXPLORE_PPTJayeshShete1
Ã˝
EXPLORE 6 EXCITING DOMAINS:
1. Machine Learning: Discover the world of AI and ML!
2. App Development: Build innovative mobile apps!
3. Competitive Programming: Enhance your coding skills!
4. Web Development: Create stunning web applications!
5. Blockchain: Uncover the power of decentralized tech!
6. Cloud Computing: Explore the world of cloud infrastructure!
Join us to unravel the unexplored, network with like-minded individuals, and dive into the world of tech!Integration of Additive Manufacturing (AM) with IoT : A Smart Manufacturing A...



Integration of Additive Manufacturing (AM) with IoT : A Smart Manufacturing A...ASHISHDESAI85
Ã˝
Combining 3D printing with Internet of Things (IoT) enables the creation of smart, connected, and customizable objects that can monitor, control, and optimize their performance, potentially revolutionizing various industries. oT-enabled 3D printers can use sensors to monitor the quality of prints during the printing process. If any defects or deviations from the desired specifications are detected, the printer can adjust its parameters in real time to ensure that the final product meets the required standards.Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdf



Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdfWater Industry Process Automation & Control
Ã˝
Welcome to the March 2025 issue of WIPAC Monthly the magazine brought to you by the LinkedIn Group WIPAC Monthly.
In this month's edition, on top of the month's news from the water industry we cover subjects from the intelligent use of wastewater networks, the use of machine learning in water quality as well as how, we as an industry, need to develop the skills base in developing areas such as Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence.
Enjoy the latest editionEnv and Water Supply Engg._Dr. Hasan.pdf



Env and Water Supply Engg._Dr. Hasan.pdfMahmudHasan747870
Ã˝
Core course, namely Environment and Water Supply Engineering. Full lecture notes are in book format for the BSc in Civil Engineering program. How to Build a Maze Solving Robot Using Arduino



How to Build a Maze Solving Robot Using ArduinoCircuitDigest
Ã˝
Learn how to make an Arduino-powered robot that can navigate mazes on its own using IR sensors and "Hand on the wall" algorithm.
This step-by-step guide will show you how to build your own maze-solving robot using Arduino UNO, three IR sensors, and basic components that you can easily find in your local electronics shop.autonomous vehicle project for engineering.pdf



autonomous vehicle project for engineering.pdfJyotiLohar6
Ã˝
autonomous vehicle project for engineeringLessons learned when managing MySQL in the Cloud



Lessons learned when managing MySQL in the CloudIgor Donchovski
Ã˝
Managing MySQL in the cloud introduces a new set of challenges compared to traditional on-premises setups, from ensuring optimal performance to handling unexpected outages. In this article, we delve into covering topics such as performance tuning, cost-effective scalability, and maintaining high availability. We also explore the importance of monitoring, automation, and best practices for disaster recovery to minimize downtime.US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...



US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...Thane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
Ã˝
Preface: The ReGenX Generator innovation operates with a US Patented Frequency Dependent Load
Current Delay which delays the creation and storage of created Electromagnetic Field Energy around
the exterior of the generator coil. The result is the created and Time Delayed Electromagnetic Field
Energy performs any magnitude of Positive Electro-Mechanical Work at infinite efficiency on the
generator's Rotating Magnetic Field, increasing its Kinetic Energy and increasing the Kinetic Energy of
an EV or ICE Vehicle to any magnitude without requiring any Externally Supplied Input Energy. In
Electricity Generation applications the ReGenX Generator innovation now allows all electricity to be
generated at infinite efficiency requiring zero Input Energy, zero Input Energy Cost, while producing
zero Greenhouse Gas Emissions, zero Air Pollution and zero Nuclear Waste during the Electricity
Generation Phase. In Electric Motor operation the ReGen-X Quantum Motor now allows any
magnitude of Work to be performed with zero Electric Input Energy.
Demonstration Protocol: The demonstration protocol involves three prototypes;
1. Protytpe #1, demonstrates the ReGenX Generator's Load Current Time Delay when compared
to the instantaneous Load Current Sine Wave for a Conventional Generator Coil.
2. In the Conventional Faraday Generator operation the created Electromagnetic Field Energy
performs Negative Work at infinite efficiency and it reduces the Kinetic Energy of the system.
3. The Magnitude of the Negative Work / System Kinetic Energy Reduction (in Joules) is equal to
the Magnitude of the created Electromagnetic Field Energy (also in Joules).
4. When the Conventional Faraday Generator is placed On-Load, Negative Work is performed and
the speed of the system decreases according to Lenz's Law of Induction.
5. In order to maintain the System Speed and the Electric Power magnitude to the Loads,
additional Input Power must be supplied to the Prime Mover and additional Mechanical Input
Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft.
6. For example, if 100 Watts of Electric Power is delivered to the Load by the Faraday Generator,
an additional >100 Watts of Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive
Shaft by the Prime Mover.
7. If 1 MW of Electric Power is delivered to the Load by the Faraday Generator, an additional >1
MW Watts of Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft by the
Prime Mover.
8. Generally speaking the ratio is 2 Watts of Mechanical Input Power to every 1 Watt of Electric
Output Power generated.
9. The increase in Drive Shaft Mechanical Input Power is provided by the Prime Mover and the
Input Energy Source which powers the Prime Mover.
10. In the Heins ReGenX Generator operation the created and Time Delayed Electromagnetic Field
Energy performs Positive Work at infinite efficiency and it increases the Kinetic Energy of the
system.
Turbocor Product and Technology Review.pdf



Turbocor Product and Technology Review.pdfTotok Sulistiyanto
Ã˝
High Efficiency Chiller System in HVACWater Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdf



Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdfWater Industry Process Automation & Control
Ã˝
US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...



US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...Thane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
Ã˝
x-raydiffraction
- 1. X – RAY DIFFRACTION (XRD) K V GOPINATH M Pharm PhD,CPhT Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams TIRUPATI e-mail:gopinath.karnam@gmail.com
- 2. Introduction  It is a novel & non destructive method of chemical analysis and a variety of x –ray techniques are available in practice.  These are : X – Ray Absorption : X-ray diffraction X-ray Fluorescence  X – ray diffraction “ Every crystalline substance gives a pattern; the same substance always gives the same pattern; and in a mixture of substances each produces its pattern independently of the others”  The X-ray diffraction pattern of a pure substance is, therefore, like a fingerprint of the substance. It is based on the scattering of x-rays by crystals.  Definition The atomic planes of a crystal cause an incident beam of X- rays to interfere with one another as they leave the crystal. The phenomenon is called X-ray diffraction.
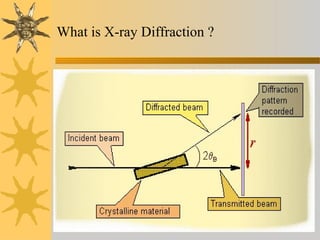
- 3. What is X-ray Diffraction ?
- 4. Why XRD?  Measure the average spacing's between layers or rows of atoms  Determine the orientation of a single crystal or grain  Find the crystal structure of an unknown material  Measure the size, shape and internal stress of small crystalline regions
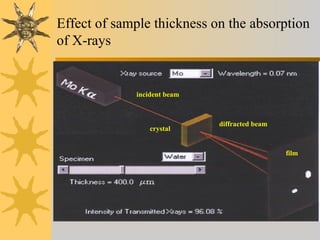
- 5. Effect of sample thickness on the absorption of X-rays diffracted beam film incident beam crystal
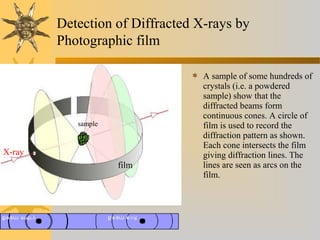
- 6. Detection of Diffracted X-rays by Photographic film  A sample of some hundreds of crystals (i.e. a powdered sample) show that the diffracted beams form continuous cones. A circle of film is used to record the diffraction pattern as shown. Each cone intersects the film giving diffraction lines. The lines are seen as arcs on the film. sample film X-ray
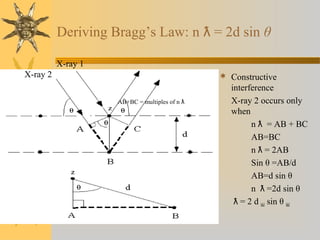
- 7. Bragg’s Law and Diffraction  How waves reveal the atomic structure of crystals N = 2d sin ƛ θ N = integer  Diffraction occurs only when Bragg’s Law is satisfied Condition for constructive interference (X-rays 1 & 2) from planes with spacing d Atomic plane
- 8. Deriving Bragg’s Law: n ƛ = 2d sin θ  Constructive interference X-ray 2 occurs only when n = AB + BC ƛ AB=BC n = 2AB ƛ Sin θ =AB/d AB=d sin θ n =2d sin ƛ θ = 2 d ƛ hkl sin θ hkl X-ray 2 X-ray 1 AB+BC = multiples of n ƛ
- 9. Planes in Crystals-2 dimension  Different planes have different spacing  To satisfy Bragg’s Law, q must change as d changes e.g., q decreases as d increases.
- 10. Basics of Crystallography  The atoms are arranged in a regular pattern, and there is as smallest volume element that by repetition in three dimensions describes the crystal. This smallest volume element is called a unit cell.  Crystals consist of planes of atoms that are spaced a distance d apart, but can be resolved into many atomic planes, each with a different d spacing.  The dimensions of the unit cell is described by three axes : a, b, c and the angles between them α, β , and γ are lattice constants which can be determined by XRD. Lattice
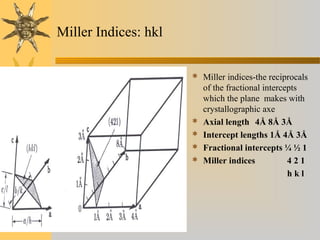
- 11. Miller Indices: hkl  Miller indices-the reciprocals of the fractional intercepts which the plane makes with crystallographic axe  Axial length 4Å 8Å 3Å  Intercept lengths 1Å 4Å 3Å  Fractional intercepts ¼ ½ 1  Miller indices 4 2 1 h k l
- 12. Production of X-rays  X-rays are produced whenever high-speed electrons collide with a metal target.  A source of electrons – hot W filament, a high accelerating voltage between the cathode (W) and the anode and a metal target, Cu, Al, Mo, Mg.  The anode is a water-cooled block of Cu containing desired target metal.
- 13. Specimen Preparation  Powders: 0.1μm < particle size < 40 μm Peak broadening less diffraction occurring  Bulks: smooth surface after polishing, specimens should be thermal annealed to eliminate any surface deformation induced during polishing.
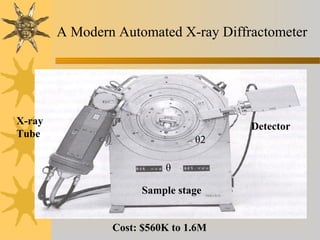
- 14. A Modern Automated X-ray Diffractometer X-ray Tube Detector Sample stage θ θ2 Cost: $560K to 1.6M
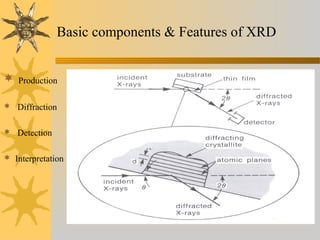
- 15. Basic components & Features of XRD  Production  Diffraction  Detection  Interpretation
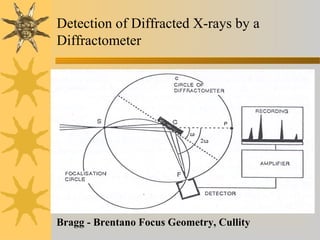
- 16. Detection of Diffracted X-rays by a Diffractometer Bragg - Brentano Focus Geometry, Cullity
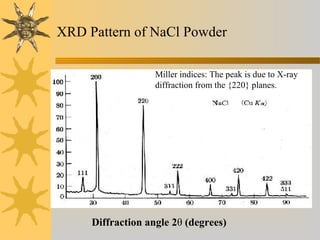
- 17. XRD Pattern of NaCl Powder Diffraction angle 2θ (degrees) Miller indices: The peak is due to X-ray diffraction from the {220} planes.
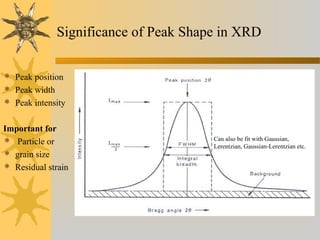
- 18. Significance of Peak Shape in XRD  Peak position  Peak width  Peak intensity Important for  Particle or  grain size  Residual strain Can also be fit with Gaussian, Lerentzian, Gaussian-Lerentzian etc.
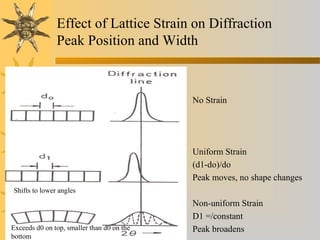
- 19. Effect of Lattice Strain on Diffraction Peak Position and Width No Strain Uniform Strain (d1-do)/do Peak moves, no shape changes Non-uniform Strain D1 =/constant Peak broadens Shifts to lower angles Exceeds d0 on top, smaller than d0 on the bottom
- 20. Applications of XRD  XRD is a non destructive technique to identify crystalline phases and orientation - Obtain XRD pattern ; Measure d-spacings ; Obtain integrated intensities ; - Compare data with known standards in the JCPDS file  To determine structural properties: - Lattice parameters (10-4Å),, grain size, expitaxy, phase composition, prefer strained orientation (Laue) order-disorder transformation, thermal expansion  To measure thickness of thin films and multi-layers*  To determine atomic arrangement  Detection limits: ~3% in a two phase mixture; can be ~0.1% with synchrotron radiation Spatial resolution: normally none
- 21. Applications of XRD  The electron density and accordingly, the position of the atoms in complex structures, such as penicillin may be determined from a comprehensive mathematical study of the x-ray diffraction pattern.  The elucidation of structure of penicillin by xrd paved the way for the later synthesis of penicillin.  The powder xrd pattern may be thought of as finger print of the single crystal structure, and it may be used conduct qualitative and quantitative analysis.  Xrd can also be used to determine whether the compound is solvated or not
- 22. Applications of XRD  Particle size determination by applying the relation. v= V. δθ. cos θ / 2n Where v = the volume or size of an individual crystalline V= the total volume of the specimen irradiated n = the number of spots in a deffraction ring at a Bragg angle θ δθ = the divergence of the X –ray beam  Determination of Cis-Trans isomerism  It is used to assess the weathering and degradation of natural and synthetic , minerals.  Tooth enamel and dentine have been examined by xrd.  State of anneal in metals
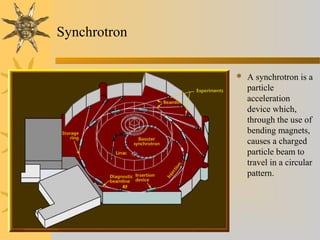
- 23. Synchrotron  A synchrotron is a particle acceleration device which, through the use of bending magnets, causes a charged particle beam to travel in a circular pattern.
- 24. Advantages of using synchrotron radiation  Detecting the presence and quantity of trace elements  Providing images that show the structure of materials  Producing X-rays with 108 more brightness than those from normal X-ray tube (tiny area of sample)  Having the right energies to interact with elements in light atoms such as carbon and oxygen  Producing X-rays with wavelengths (tunable) about the size of atom, molecule and chemical bonds
- 25. Instrumental Sources of Error  Specimen displacement  Instrument misalignment  Error in zero 2 θ position  Peak distortion due to K alfa 2 and K beta wavelengths
- 26. Conclusions  Non-destructive, fast, easy sample preparation  High-accuracy for d-spacing calculations  Can be done in-situ  Single crystal, poly, and amorphous materials  Standards are available for thousands of material systems






















