6.pulmonary edema and ards
- 1. 1 CHA├ģN ├æOA├ÖN H├īNH A├øNH PHU├ś PHO├ģI CA├üP VA├ś HO├äI CH├¢├ÖNG NGUY CA├üP HO├é HA├üP ├ö├ø NG├¢├ö├śI L├ö├ÖN BS.NGUYE├āN QUY├Ö KHOA├ÖNG BS.NGUYE├āN QUANG TRO├ÅNG
- 2. 2 DA├śN BA├śI ’ü« Nha├żp ├▒e├Ā. ’ü« Be├żnh ly├╣ phe├Ī nang lan to├╗a. ’ü« X quang Phu├Ė pho├źi ca├Īp. ’ü« X quang Ho├żi ch├Č├╣ng nguy ca├Īp ho├ó ha├Īp ├┤├╗ ng├Č├┤├Ėi l├┤├╣n. ’ü« Sinh ly├╣ be├żnh cu├╗a Phu├Ė pho├źi ca├Īp va├Ė ARDS. ’ü« To├╣m ta├®t.
- 3. 3 NHA├äP ├æE├Ć ’ü« Phu├Ė pho├źi ca├Īp (Acute pulmonary edema) va├Ė Ho├żi ch├Č├╣ng nguy ca├Īp ├┤├╗ ng├Č├┤├Ėi l├┤├╣n (Adult respiratory distress syndrome- ARDS) la├Ė hai be├żnh ly├╣ th├Č├┤├Ėng ga├½p ta├»i ca├╣c pho├Ėng Sa├¬n so├╣c ├▒a├½c bie├żt va├Ė Ho├Āi s├Č├╣c ngoa├»i. ’ü« Co├╣ nh├Č├Ąng da├Īu hie├żu la├óm sa├Ėng va├Ė X quang de├Ż la├Żn lo├żn.
- 4. NHA├äP ├æE├Ć ’ü« Bie├źn hie├żn ba├©ng s├Č├» tu├» d├▓ch trong ca├╣c phe├Ī nang mo├żt ca├╣ch lan to├╗a. ’ü« Phu├Ė pho├źi ca├Īp th├Č├┤├Ėng ga├½p h├┤n,tie├ón l├Č├┤├»ng kha├╗ quan ne├Īu ├▒ie├Āu tr├▓ s├┤├╣m. ’ü« ARDS hie├Īm ga├½p h├┤n nh├Čng tie├ón l├Č├┤├»ng ra├Īt xa├Īu ma├½c du├Ė co├╣ ├▒ie├Āu tr├▓.
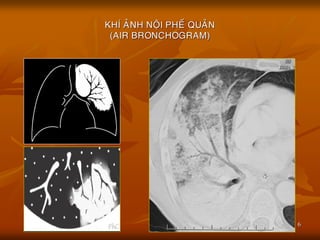
- 5. 5 BE├äNH LY├Ö PHE├ü NANG LAN TO├øA ├æA├ŗC ├æIE├ģM CU├øA TO├ģN TH├¢├öNG PHE├ü NANG ’ü« Nhie├Āu ├▒a├╣m m├┤├Ė ma├żt ├▒o├ż n├Č├┤├╣c,b├┤├Ė kho├óng ro├Ą, de├Ż ho├żi tu├» v├┤├╣i nhau. ’ü« Co├╣ kh├Ł a├╗nh no├żi phe├Ī qua├╗n (air bronchogram) hoa├½c h├¼nh ca├╣nh b├Č├┤├╣m (ButterflyŌĆÖs wings). ’ü« Xo├╣a m├┤├Ė ca├╣c ma├»ch ma├╣u va├Ė b├┤├Ė tim. ’ü« Th├Č├┤├Ėng thay ├▒o├źi nhanh theo th├┤├Ėi gian.
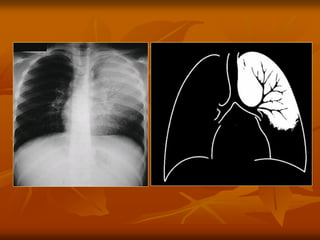
- 6. 6 KH├Ź A├øNH NO├äI PHE├ü QUA├øN (AIR BRONCHOGRAM)
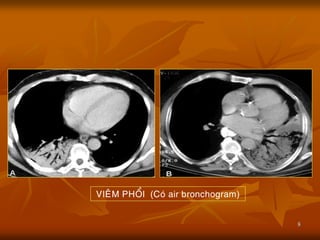
- 8. 8 VIE├éM PHO├ģI (Co├╣ air bronchogram)
- 9. ’ü« Gi├Ī trß╗ŗ lß╗øn nhß║źt m├Ā dß║źu hiß╗ću n├Āy ─æem l├Ā, ─æ├│ l├Ā khi c├│ Air bronchogram sign (+) th├¼ ta c├│ thß╗ā khß║│ng ─æß╗ŗnh tß╗Ģn thŲŻŲĪng ß╗¤ nhu m├┤ ▒Ķ│¾ß╗Ģi, loß║Īi trß╗½ tß╗Ģn thŲŻŲĪng c├│ nguß╗ōn gß╗æc tß╗½ m├Āng ▒Ķ│¾ß╗Ģi, tß╗½ th├Ānh ngß╗▒c, c┼®ng nhŲŻ tß╗½ trung thß║źt. ’ü« Dß║źu hiß╗ću kh├Ł ß║Żnh nß╗Öi phß║┐ quß║Żn thŲŻß╗Øng gß║Ęp nhß║źt trong Vi├¬m ▒Ķ│¾ß╗Ģi, nhŲŻng c┼®ng c├│ thß╗ā gß║Ęp trong c├Īc bß╗ćnh l├Į kh├Īc nhŲŻ Ph├╣ ▒Ķ│¾ß╗Ģi, Nhß╗ōi m├Īu ▒Ķ│¾ß╗Ģi, thß║Łm ch├Ł cß║Ż trong bŲŻß╗øu ▒Ķ│¾ß╗Ģi (bronchioloalveolar carcinoma, lymphoma).
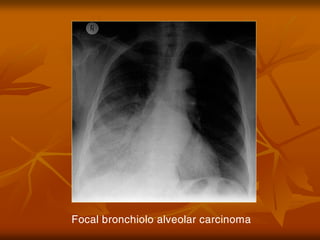
- 10. Focal bronchiolo alveolar carcinoma
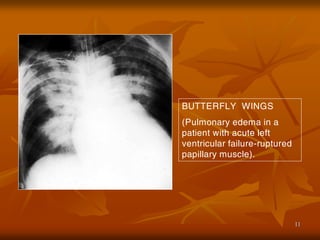
- 11. 11 BUTTERFLY WINGS (Pulmonary edema in a patient with acute left ventricular failure-ruptured papillary muscle).
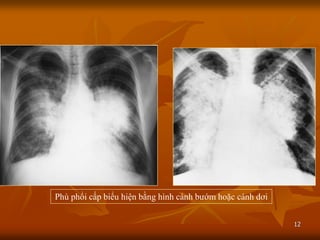
- 12. 12 Ph├╣ ▒Ķ│¾ß╗Ģi cß║źp biß╗āu hiß╗ćn bß║▒ng h├¼nh c├Īnh bŲŻß╗øm hoß║Ęc c├Īnh dŲĪi
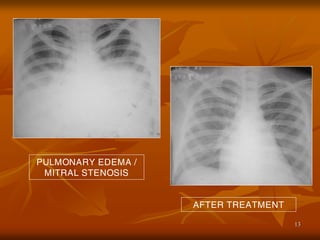
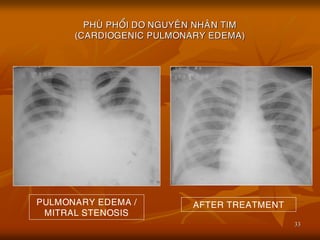
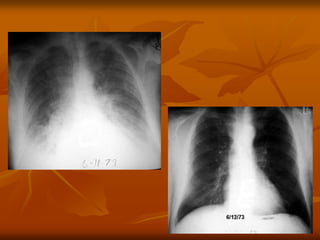
- 13. 13 PULMONARY EDEMA / MITRAL STENOSIS AFTER TREATMENT
- 14. 14 BE├äNH LY├Ö PHE├ü NANG LAN TO├øA ├æA├ŗC ├æIE├ģM CU├øA TO├ģN TH├¢├öNG PHE├ü NANG ’ü« Tre├ón th├Č├»c te├Ī,ca├╣c to├źn th├Č├┤ng phe├Ī nang lan to├╗a th├Č├┤├Ėng kho├óng ├▒a├½c hie├żu cho mo├żt be├żnh ly├╣ na├Ėo ca├╗. Ly├╣ do la├Ė co├╣ nhie├Āu cha├Īt co├╣ the├ź tra├╣m ├▒a├Āy ca├╣c phe├Ī nang nh├Č:d├▓ch,ma├╣u,mu├╗,protein,te├Ī ba├ĖoŌĆ”
- 15. 15 BE├äNH LY├Ö PHE├ü NANG LAN TO├øA CA├ÖC NGUYE├éN NHA├éN CH├ŹNH ’ü« 1/ Phu├Ė pho├źi ca├Īp do be├żnh ly├╣ tim. ’ü« 2/ Phu├Ė pho├źi kho├óng do be├żnh tim. ’ü« 3/ Ho├żi ch├Č├╣ng nguy ca├Īp ho├ó ha├Īp ├┤├╗ ng├Č├┤├Ėi l├┤├╣n. ’ü« 4/ Xuß║źt huyß║┐t trong ▒Ķ│¾ß╗Ģi (Cha├Īn th├Č├┤ng ng├Č├»c lan to├╗a).
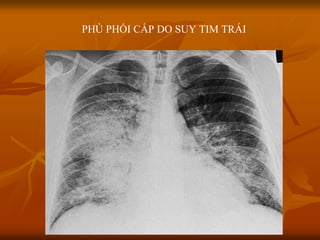
- 16. PH├Ö PHß╗öI Cß║żP DO SUY TIM TR├üI
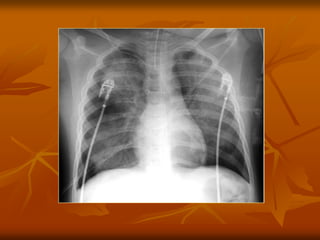
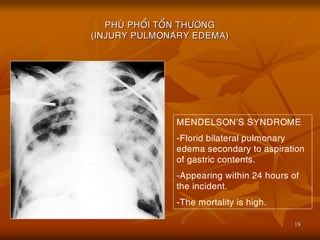
- 18. 18 PHU├ś PHO├ģI TO├ģN TH├¢├öNG (INJURY PULMONARY EDEMA) MENDELSONŌĆÖS SYNDROME -Florid bilateral pulmonary edema secondary to aspiration of gastric contents. -Appearing within 24 hours of the incident. -The mortality is high.
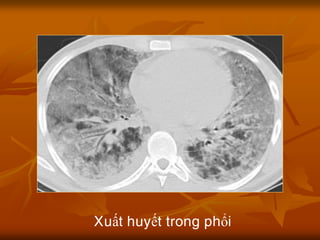
- 19. Xuß║źt huyß║┐t trong ▒Ķ│¾ß╗Ģi
- 20. 20 BE├äNH LY├Ö PHE├ü NANG LAN TO├øA CA├ÖC NGUYE├éN NHA├éN CH├ŹNH ’ü« 5/ Vie├óm phe├Ī qua├╗n pho├źi do nhie├Żm tru├Ėng. ’ü« 6/ Bß╗ćnh m├Āng trong (Membrane hyaline) v├Ā Bß╗ćnh ─æß╗Źng protein trong phe├Ī nang (proteinose alve├╣olaire). ’ü« 7/ Ung th├Č tie├źu phe├Ī qua├╗n-phe├Ī nang (cancer bronchiolo-alve├╣olaire).
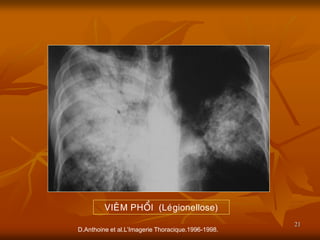
- 21. 21 D.Anthoine et al.LŌĆÖImagerie Thoracique.1996-1998. VIE├éM PHO├ģI (Le├╣gionellose)
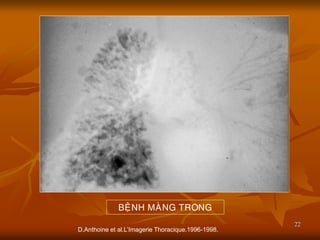
- 22. 22 D.Anthoine et al.LŌĆÖImagerie Thoracique.1996-1998. BE├äNH MA├śNG TRONG
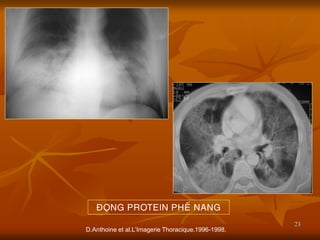
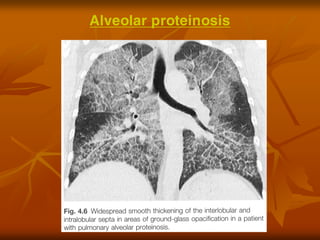
- 23. 23 D.Anthoine et al.LŌĆÖImagerie Thoracique.1996-1998. ├æO├ÅNG PROTEIN PHE├ü NANG
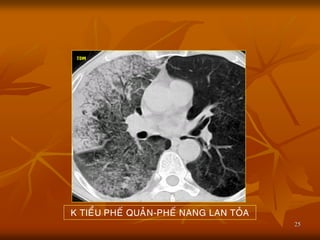
- 25. 25 K TIE├ģU PHE├ü QUA├øN-PHE├ü NANG LAN TO├øA
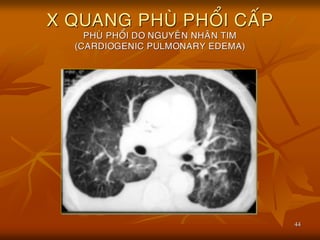
- 26. 26 X QUANG PHU├ś PHO├ģI CA├üP ’ü« Ha├żu qua├╗ cu├╗a s├Č├» ├Č├╣ d├▓ch trong mo├ó ke├Ą cu├╗a pho├źi,va├Ė ne├Īu na├½ng h├┤n th├¼ d├▓ch tra├Ėn va├Ėo phe├Ī nang. ’ü« H├¼nh X quang cu├╗a phu├Ė pho├źi tu├Ėy thuo├żc va├Ėo m├Č├╣c ├▒o├ż d├▓ch na├Ėy:thay ├▒o├źi t├Č├Ė h├¼nh m├┤├Ė ma├Ėu k├Łnh ├▒u├»c cho ├▒e├Īn h├¼nh ├▒u├»c da├»ng ca├╣nh b├Č├┤├╣m. ’ü« Nguye├ón nha├ón co├╣ the├ź do tim hoa├½c kho├óng do tim.
- 27. 27 X QUANG PHU├ś PHO├ģI CA├üP PHU├ś PHO├ģI DO NGUYE├éN NHA├éN TIM (CARDIOGENIC PULMONARY EDEMA) ’ü« Chu├╗ ye├Īu do Suy tim tra├╣i. ’ü« Bie├źu hie├żn s├┤├╣m tre├ón X quang la├Ė s├Č├» ta├╣i pha├ón pho├Īi ma├»ch ma├╣u pho├źi le├ón thu├Ėy tre├ón hai pho├źi. ’ü« Ne├Īu Suy tim tra├╣i tie├Īp die├Żn,ta se├Ą tha├Īy ma├»ch ma├╣u pho├źi m├┤├Ė do d├▓ch tha├Īm quanh ma├»ch ma├╣u, ke├Ėm theo la├Ė ca├╣c ├▒├Č├┤├Ėng Kerley.
- 28. H├īNH ß║óNH Mß║ČT K├ŹNH Mß╗£ (GROUND-GLASS PATTERN) ’ü« Gß╗Źi l├Ā h├¼nh ß║Żnh mß║Ęt k├Łnh mß╗Ø khi c├│ sß╗▒ gia t─āng ─æß║Łm ─æß╗Ö nhu m├┤ ▒Ķ│¾ß╗Ģi, trong khi vß║½n thß║źy r├Ą bß╗Ø mß║Īch m├Īu v├Ā phß║┐ quß║Żn. H├¼nh ß║Żnh mß║Ęt k├Łnh mß╗Ø c├│ khi kß║┐t hß╗Żp vß╗øi dß║źu hiß╗ću kh├Ł ß║Żnh nß╗Öi phß║┐ quß║Żn (air bronchogram). ’ü« Cß║¦n phß║Żi ph├ón biß╗ćt vß╗øi ─æ├┤ng ─æß║Ęc ▒Ķ│¾ß╗Ģi (consolidation): bß╗Ø mß║Īch m├Īu-phß║┐ quß║Żn bß╗ŗ xo├Ī. ’ü« ─É├óy l├Ā h├¼nh ß║Żnh thŲŻß╗Øng gß║Ęp nhŲŻng kh├┤ng ─æß║Ęc hiß╗ću, thŲŻß╗Øng gß║Ęp ß╗¤ xuß║źt huyß║┐t ▒Ķ│¾ß╗Ģi (pulmonary hemorrhage), ph├╣ ▒Ķ│¾ß╗Ģi (pulmonary edema), vi├¬m ▒Ķ│¾ß╗Ģi.
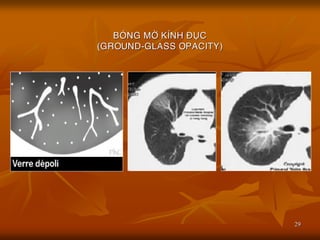
- 29. 29 BO├ÖNG M├ö├ś K├ŹNH ├æU├ÅC (GROUND-GLASS OPACITY)
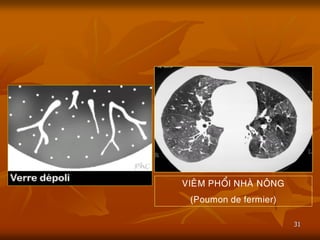
- 31. 31 VIE├éM PHO├ģI NHA├ś NO├éNG (Poumon de fermier)
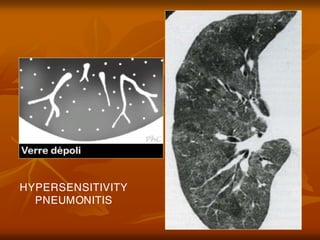
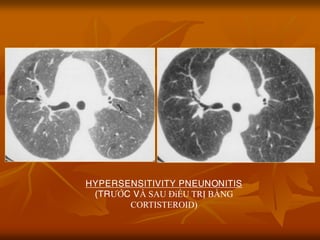
- 32. HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUNONITIS (TRŲóß╗ÜC V├Ć SAU ─Éiß╗ĆU TRß╗Ŗ Bß║░NG CORTISTEROID)
- 33. 33 PHU├ś PHO├ģI DO NGUYE├éN NHA├éN TIM (CARDIOGENIC PULMONARY EDEMA) PULMONARY EDEMA / MITRAL STENOSIS AFTER TREATMENT
- 34. 34 X QUANG PHU├ś PHO├ģI CA├üP PHU├ś PHO├ģI DO NGUYE├éN NHA├éN TIM (CARDIOGENIC PULMONARY EDEMA) ’ü« Na├½ng h├┤n,ta se├Ą tha├Īy tu├» d├▓ch trong ca├╣c chu├Ėm phe├Ī nang ├┤├╗ hai ├▒a├╣y pho├źi,ro├Āi tu├» d├▓ch phe├Ī nang quanh hai ro├Īn pho├źi cho ra h├¼nh ca├╣nh b├Č├┤├╣m. ’ü« Co├╣ the├ź tra├Ėn d├▓ch ra├Ąnh lie├ón thu├Ėy,tra├Ėn d├▓ch ma├Ėng pho├źi.
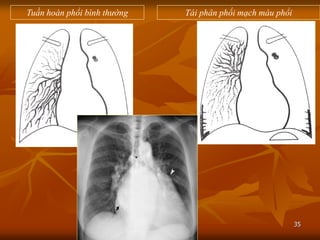
- 35. 35 Tuß║¦n ho├Ān ▒Ķ│¾ß╗Ģi b├¼nh thŲ░ß╗Øng T├Īi ph├ón phß╗æi mß║Īch m├Īu ▒Ķ│¾ß╗Ģi
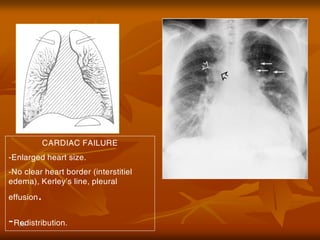
- 36. 36 CARDIAC FAILURE -Enlarged heart size. -No clear heart border (interstitiel edema), KerleyŌĆÖs line, pleural effusion. -Redistribution.
- 37. 37
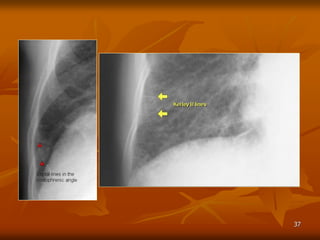
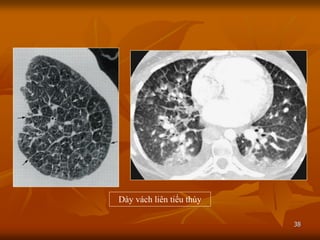
- 38. 38 D├Āy v├Īch li├¬n tiß╗āu th├╣y
- 39. 39 X QUANG PHU├ś PHO├ģI CA├üP PHU├ś PHO├ģI DO NGUYE├éN NHA├éN TIM (CARDIOGENIC PULMONARY EDEMA) DA├üU HIE├äU KHO├éNG CHUYE├éN BIE├äT DA├üU HIE├äU CHUYE├éN BIE├äT 1ŌĆÖ.Phu├Ė quanh tru├»c ma├»ch ma├╣u-phe├Ī qua├╗n. 2ŌĆÖ.Tra├Ėn d├▓ch ra├Ąnh lie├ón thu├Ėy. 3ŌĆÖ.Tra├Ėn d├▓ch ma├Ėng pho├źi. 1.Ta├╣i pha├ón pho├Īi ma├»ch ma├╣u pho├źi. 2.Pha├ón bo├Ī h├¼nh ca├╣nh b├Č├┤├╣m. 3.├æ├Č├┤├Ėng Kerley B.
- 40. 40 X QUANG PHU├ś PHO├ģI CA├üP PHU├ś PHO├ģI DO NGUYE├éN NHA├éN TIM (CARDIOGENIC PULMONARY EDEMA)
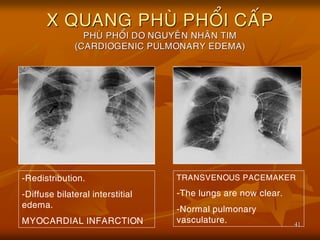
- 41. 41 X QUANG PHU├ś PHO├ģI CA├üP PHU├ś PHO├ģI DO NGUYE├éN NHA├éN TIM (CARDIOGENIC PULMONARY EDEMA) -Redistribution. -Diffuse bilateral interstitial edema. MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION TRANSVENOUS PACEMAKER -The lungs are now clear. -Normal pulmonary vasculature.
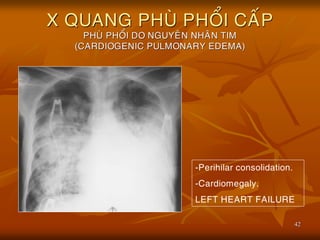
- 42. 42 X QUANG PHU├ś PHO├ģI CA├üP PHU├ś PHO├ģI DO NGUYE├éN NHA├éN TIM (CARDIOGENIC PULMONARY EDEMA) -Perihilar consolidation. -Cardiomegaly. LEFT HEART FAILURE
- 43. 43
- 44. 44 X QUANG PHU├ś PHO├ģI CA├üP PHU├ś PHO├ģI DO NGUYE├éN NHA├éN TIM (CARDIOGENIC PULMONARY EDEMA)
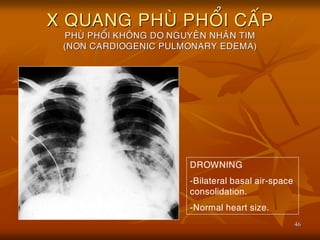
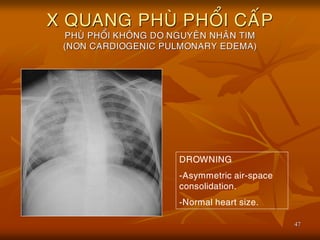
- 45. 45 X QUANG PHU├ś PHO├ģI CA├üP PHU├ś PHO├ģI KHO├éNG DO NGUYE├éN NHA├éN TIM (NON CARDIOGENIC PULMONARY EDEMA) ’ü« Nguye├ón nha├ón:co├╣ nh├Č├Ąng nguye├ón nha├ón nh├Č:Ngo├żp n├Č├┤├╣c,Ure├ó huye├Īt cao,truye├Ān d├▓ch qua├╣ ta├╗i,chß║źn thŲŻŲĪng sß╗Ź n├ŻoŌĆ” ’ü« Ca├╣c nguye├ón nha├ón tre├ón ga├óy ta├¬ng t├Łnh tha├Īm tha├Ėnh ma├»ch va├Ė thoa├╣t d├▓ch va├Ėo phe├Ī nang. ’ü« H├¼nh a├╗nh bo├╣ng m├┤├Ė phe├Ī nang,th├Č├┤├Ėng co├╣ h├¼nh ca├╣nh b├Č├┤├╣m trong khi bo├╣ng tim b├¼nh th├Č├┤├Ėng.
- 46. 46 X QUANG PHU├ś PHO├ģI CA├üP PHU├ś PHO├ģI KHO├éNG DO NGUYE├éN NHA├éN TIM (NON CARDIOGENIC PULMONARY EDEMA) DROWNING -Bilateral basal air-space consolidation. -Normal heart size.
- 47. 47 X QUANG PHU├ś PHO├ģI CA├üP PHU├ś PHO├ģI KHO├éNG DO NGUYE├éN NHA├éN TIM (NON CARDIOGENIC PULMONARY EDEMA) DROWNING -Asymmetric air-space consolidation. -Normal heart size.
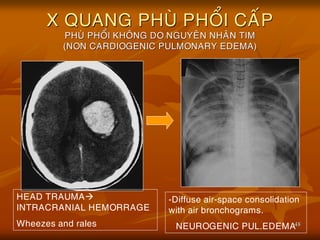
- 48. 48 X QUANG PHU├ś PHO├ģI CA├üP PHU├ś PHO├ģI KHO├éNG DO NGUYE├éN NHA├éN TIM (NON CARDIOGENIC PULMONARY EDEMA) -Diffuse air-space consolidation with air bronchograms. NEUROGENIC PUL.EDEMA HEAD TRAUMA’āĀ INTRACRANIAL HEMORRAGE Wheezes and rales
- 49. 49 X QUANG ARDS PHU├ś PHO├ģI TO├ģN TH├¢├öNG (INJURY PULMONARY EDEMA) ’ü« Khoa├╗ng 150.000 be├żnh nha├ón/na├¬m (├┤├╗ Hoa ky├Ė) v├┤├╣i t├Č├╗ vong # 60%. ’ü« Ca├╣c nguye├ón nha├ón nh├Č:Nhie├Żm tru├Ėng, ha├» huye├Īt a├╣p,h├Łt ca├╣c cha├Īt ├▒o├żcŌĆ”co├╣ the├ź la├Ėm to├źn th├Č├┤ng no├żi ba├Ėo mao ma├»ch va├Ė lie├ón ba├Ėo phe├Ī nang ga├óy ne├ón tie├Īt d├▓ch va├Ėo phe├Ī nang va├Ė suy ho├ó ha├Īp na├½ng.
- 50. 50 X QUANG ARDS PHU├ś PHO├ģI TO├ģN TH├¢├öNG (INJURY PULMONARY EDEMA) ’ü« Co├╣ 9 tie├óu chua├źn cu├╗a PETTY ├▒e├ź cha├źn ├▒oa├╣n ARDS,trong ├▒o├╣ ne├ón l├Ču y├╣: ’ü« Kho├óng co├╣ t├¼nh tra├»ng Suy tim tra├╣i hoa├½c COPD. ’ü« A├Öp l├Č├»c mao ma├»ch pho├źi <12mmHg. ’ü« Co├╣ t├¼nh tra├»ng thie├Īu O2, trong ma├╣u tra├Ām tro├»ng:PaO2 Ōēż 50mmHg ma├½c du├Ė be├żnh nha├ón ├▒├Č├┤├»c ├▒├Ča O2 h├Łt va├Ėo FiO2 > 60%.
- 51. 51 X QUANG ARDS PHU├ś PHO├ģI TO├ģN TH├¢├öNG (INJURY PULMONARY EDEMA) DA├üU HIE├äU KHO├éNG CHUYE├éN BIE├äT DA├üU HIE├äU CHUYE├éN BIE├äT 1ŌĆÖ.Kho├óng phu├Ė quanh tru├»c ma├»ch ma├╣u-phe├Ī qua├╗n. 2ŌĆÖ.M├┤├Ė ma├Ėu k├Łnh ├▒u├»c. 3ŌĆÖ.Kho├óng co├╣ Tra├Ėn d├▓ch ma├Ėng pho├źi. 1.Ma├»ch ma├╣u pho├źi kho├óng gia├Ąn to va├Ė kho├óng ├▒a├╗o ng├Č├┤├»c. 2.Phu├Ė pho├źi ra├╗i ra├╣c ├┤├╗ ngoa├»i bie├ón. 3.Tim kho├óng to
- 52. 52 X QUANG ARDS PHU├ś PHO├ģI TO├ģN TH├¢├öNG (INJURY PULMONARY EDEMA)
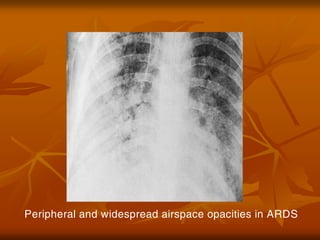
- 53. Peripheral and widespread airspace opacities in ARDS
- 54. 54 X QUANG ARDS PHU├ś PHO├ģI TO├ģN TH├¢├öNG (INJURY PULMONARY EDEMA) ’ü« Th├┤├Ėi gian: ’ü« 0-12 gi├┤├Ė’āĀX quang ng├Č├»c b├¼nh th├Č├┤├Ėng. ’ü« 12-24 gi├┤├Ė’āĀPhu├Ė pho├źi mo├ó ke├Ą cho ra h├¼nh m├┤├Ė ma├Ėu k├Łnh ├▒u├»c. ’ü« 24-48 gi├┤├Ė’āĀ├æo├óng ├▒a├½c ca├╣c chu├Ėm phe├Ī nang,ra├╗i ra├╣c chu├╗ ye├Īu ├┤├╗ ngoa├»i bie├ón. Kho├óng co├╣ TDMP ne├Īu kho├óng ke├Ėm bo├żi nhie├Żm pho├źi.
- 55. 55 X QUANG ARDS PHU├ś PHO├ģI TO├ģN TH├¢├öNG (INJURY PULMONARY EDEMA) ’ü« Th├┤├Ėi gian: ’ü« 5-7 nga├Ėy’āĀPhu├Ė pho├źi bie├Īn ma├Īt t├Č├Ė t├Č├Ė. ├æo├óng ├▒a├½c t├Č├Ėng vu├Ėng. ’ü« > 7 nga├Ėy’āĀX├┤ ho├╣a mo├ó ke├Ą.
- 56. 56 X QUANG ARDS PHU├ś PHO├ģI TO├ģN TH├¢├öNG (INJURY PULMONARY EDEMA) ’ü« Cha├źn ├▒oa├╣n pha├ón bie├żt v├┤├╣i Phu├Ė pho├źi ca├Īp ba├©ng: ’ü« ├æo a├╣p sua├Īt mao ma├»nh pho├źi b├Łt (PCWP) < 12mmHg. ’ü« Hu├╣t d├▓ch t├Č├Ė phe├Ī qua├╗n (ARDS:protein > 50g/l.)
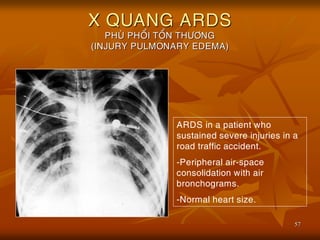
- 57. 57 X QUANG ARDS PHU├ś PHO├ģI TO├ģN TH├¢├öNG (INJURY PULMONARY EDEMA) ARDS in a patient who sustained severe injuries in a road traffic accident. -Peripheral air-space consolidation with air bronchograms. -Normal heart size.
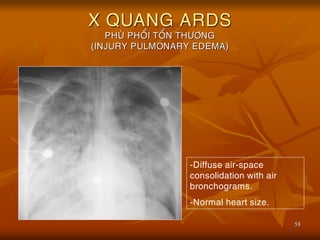
- 58. 58 X QUANG ARDS PHU├ś PHO├ģI TO├ģN TH├¢├öNG (INJURY PULMONARY EDEMA) -Diffuse air-space consolidation with air bronchograms. -Normal heart size.
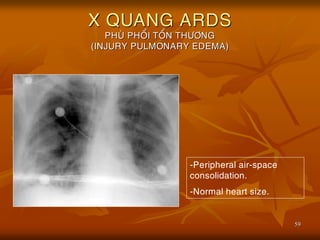
- 59. 59 X QUANG ARDS PHU├ś PHO├ģI TO├ģN TH├¢├öNG (INJURY PULMONARY EDEMA) -Peripheral air-space consolidation. -Normal heart size.
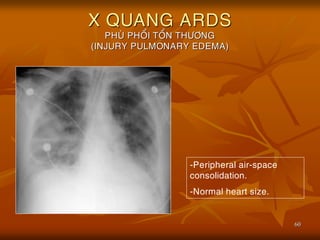
- 60. 60 X QUANG ARDS PHU├ś PHO├ģI TO├ģN TH├¢├öNG (INJURY PULMONARY EDEMA) -Peripheral air-space consolidation. -Normal heart size.
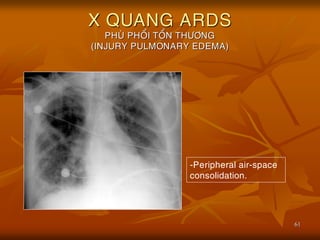
- 61. 61 X QUANG ARDS PHU├ś PHO├ģI TO├ģN TH├¢├öNG (INJURY PULMONARY EDEMA) -Peripheral air-space consolidation.
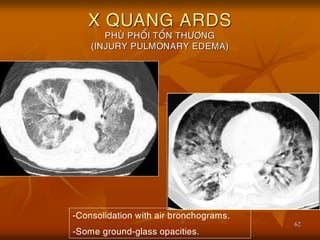
- 62. 62 X QUANG ARDS PHU├ś PHO├ģI TO├ģN TH├¢├öNG (INJURY PULMONARY EDEMA) -Consolidation with air bronchograms. -Some ground-glass opacities.
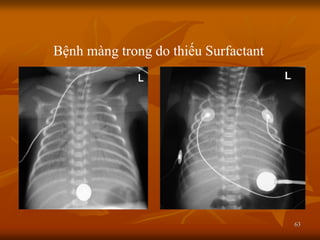
- 63. 63 Bß╗ćnh m├Āng trong do thiß║┐u Surfactant
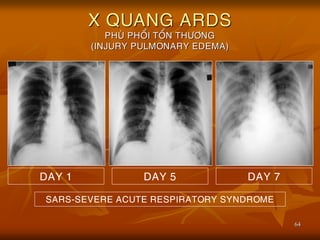
- 64. 64 X QUANG ARDS PHU├ś PHO├ģI TO├ģN TH├¢├öNG (INJURY PULMONARY EDEMA) DAY 1 DAY 5 DAY 7 SARS-SEVERE ACUTE RESPIRATORY SYNDROME
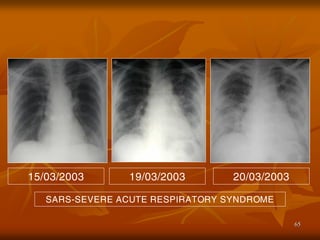
- 65. 65 SARS-SEVERE ACUTE RESPIRATORY SYNDROME 15/03/2003 19/03/2003 20/03/2003
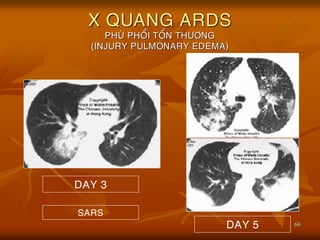
- 66. 66 X QUANG ARDS PHU├ś PHO├ģI TO├ģN TH├¢├öNG (INJURY PULMONARY EDEMA) SARS DAY 3 DAY 5
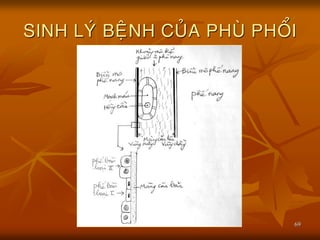
- 67. 67 SINH LY├Ö BE├äNH CU├øA PHU├ś PHO├ģI ’ü« Co├╣ 3 ye├Īu to├Ī ch├Łnh: ’ü« A├Öp sua├Īt thu├╗y t├│nh (ASTT). ’ü« A├Öp l├Č├»c keo huye├Īt t├Č├┤ng (ALKHT). ’ü« T├Łnh tha├Īm mao ma├»ch (TTMM). ’ü« Tr├Č├┤├╣c ├▒a├óy,ng├Č├┤├Ėi ta hay du├Ėng ch├Č├Ą: ŌåæASTT’āĀPhu├Ė pho├źi do tim. ŌåæTTMM’āĀPhu├Ė pho├źi kho├óng do tim.
- 68. 68 SINH LY├Ö BE├äNH CU├øA PHU├ś PHO├ģI ’ü« Nga├Ėy nay ne├ón du├Ėng: ’ü« Phu├Ė pho├źi tha├Īm (Transudative pulmonary edema) do ŌåæASTT hoa├½c ŌåōALKHT va├Ė ma├Ėng mao ma├»ch co├Ėn nguye├ón ve├»n ne├ón protein kho├óng tha├Īm qua ├▒├Č├┤├»c. ’ü« Phu├Ė pho├źi tie├Īt (Exudative pulmonary edema) do to├źn th├Č├┤ng no├żi ma├»c mao ma├»ch va├Ė bie├źu mo├ó phe├Ī nang va├Ė ŌåæTTMM ne├ón protein va├Ėo ├▒├Č├┤├»c phe├Ī nang.
- 69. 69 SINH LY├Ö BE├äNH CU├øA PHU├ś PHO├ģI
- 70. 70 SINH LY├Ö BE├äNH CU├øA PHU├ś PHO├ģI ’ü« D├Č├┤├╣i k├Łnh hie├źn vi quang ho├»c,co├╣ h├¼nh a├╗nh phu├Ė va├Ė tha├óm nhie├Żm te├Ī ba├Ėo cu├╗a va├╣ch lie├ón phe├Ī nang va├Ė khoa├╗ng ke├Ą,├▒o├Āng th├┤├Ėi co├╣ xua├Īt huye├Īt mo├ó ke├Ą va├Ė phe├Ī nang. ’ü« Ngoa├Ėi vie├żc ma├Īt ca├╣c Phe├Ī ba├Ėo type I, th├¼ th├Č├┤├Ėng tha├Īy ca├╗ t├¼nh tra├»ng ta├¬ng sa├╗n la├Żn loa├»n sa├╗n Phe├Ī ba├Ėo type II.
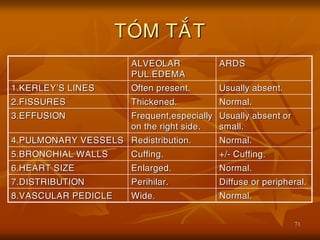
- 71. 71 TO├ÖM TA├ēT ALVEOLAR PUL.EDEMA ARDS 1.KERLEYŌĆÖS LINES Often present. Usually absent. 2.FISSURES Thickened. Normal. 3.EFFUSION Frequent,especially on the right side. Usually absent or small. 4.PULMONARY VESSELS Redistribution. Normal. 5.BRONCHIAL WALLS Cuffing. +/- Cuffing. 6.HEART SIZE Enlarged. Normal. 7.DISTRIBUTION Perihilar. Diffuse or peripheral. 8.VASCULAR PEDICLE Wide. Normal.
- 72. 72 TO├ÖM TA├ēT ALVEOLAR PULMONARY EDEMA ADULT RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME -Left heart failure. -Mitral valve disease. -Renal failure. -Overhydration. -Drowning. -Neurogenic. -Postembolic. -Sepsis. -Hypotension (ŌĆ£VietNam lungŌĆØ,ŌĆØDaNang lungŌĆØ, ŌĆØshock lungŌĆØ). -O2 toxicity. -Noxious inhalation (includes cocaine). -Aspiration. -Embolism (air,fat,amniotic). -Pancreatitis. -Disseminated intravascular coagulation. -Virulent pneumonias (SARS,Avian flu).
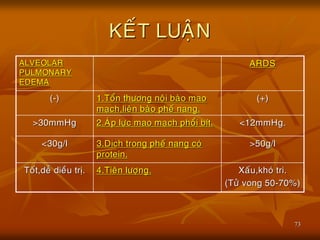
- 73. 73 KE├üT LUA├äN ALVEOLAR PULMONARY EDEMA ARDS (-) 1.To├źn th├Č├┤ng no├żi ba├Ėo mao ma├»ch,lie├ón ba├Ėo phe├Ī nang. (+) >30mmHg 2.A├Öp l├Č├»c mao ma├»ch pho├źi b├Łt. <12mmHg. <30g/l 3.D├▓ch trong phe├Ī nang co├╣ protein. >50g/l To├Īt,de├Ż die├Āu tr├▓. 4.Tie├ón l├Č├┤├»ng. Xa├Īu,kho├╣ tri. (T├Č├╗ vong 50-70%)
- 74. 74 XIN Cß║óM ŲĀN QU├Ø Vß╗Ŗ ─É├ā THEO D├ĢI